Dendritic spines: from structure to in vivo function
13-Jul-2012
EMBO reports, 2012, doi:10.1038/embor.2012.102, 13, 699 - 708 published on 13.07.2012
EMBO reports, online article
EMBO reports, online article
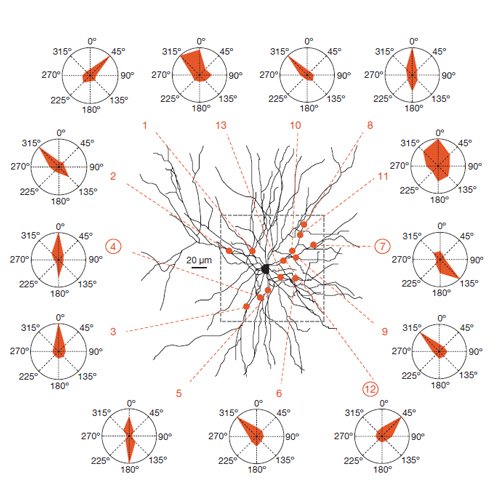
Dendritic spines arise as small protrusions from the dendritic shaft of various types of neuron and receive inputs from excitatory axons. Ever since dendritic spines were first described in the nineteenth century, questions about their function have spawned many hypotheses. In this review, we introduce understanding of the structural and biochemical properties of dendritic spines with emphasis on components studied with imaging methods. We then explore advances in in vivo imaging methods that are allowing spine activity to be studied in living tissue, from super-resolution techniques to calcium imaging. Finally, we review studies on spine structure and function in vivo. These new results shed light on the development, integration properties and plasticity of spines.