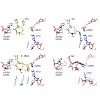
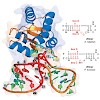
Florian Rechenmacher, Stefanie Neubauer, Carlos Mas-Moruno, Petra M. Dorfner, Julien Polleux, Judith Guasch, Bert Conings, Hans-Gerd Boyen, Alexander Bochen, Tariq R. Sobahi, Rainer Burgkart, Joachim P. Spatz, Reinhard Fässler,
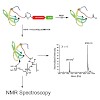
Horst KesslerWhen applied to biomolecules, solid-state NMR suffers from low sensitivity and resolution. The major obstacle to applying proton detection in the solid state is the proton dipolar network, and deuteration can help avoid this problem. In the past, researchers had primarily focused on the investigation of exchangeable protons in these systems. In this Account, we ...
|READ MORE|
Iina Laitinen, Johannes Notni, Karolin Pohle, Martina Rudelius, Eliane Farrell, Stephan G Nekolla, Gjermund Henriksen, Stefanie Neubauer,
Horst Kessler , Hans-Jürgen Wester, Markus Schwaiger
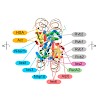
Stephanie Maria Esslinger, Björn Schwalb, Stephanie Helfer, Katharina Maria Michalik, Heidi Witte, Kerstin C. Maier, Dietmar Martin, Bernhard Michalke, Achim Tresch,
Patrick Cramer, Klaus Förstemann
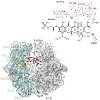
Paweł Śledź,
Pia Unverdorben,
Florian Beck,
Günter Pfeifer,
Andreas Schweitzer,
Friedrich Förster, Wolfgang Baumeister
PNAS,
2013,
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1305782110, vol. 110 no. 18,7264–7269 published on 30.04.2013
PNAS,
online article
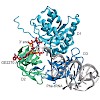
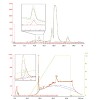
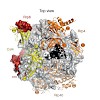
The 26S proteasome is a 2.5-MDa, ATP-dependent multisubunit proteolytic complex that processively destroys proteins carrying a degradation signal. The proteasomal ATPase heterohexamer is a key module of the 19S regulatory particle; it unfolds substrates and translocates them into the 20S core particle where degradation takes place. We used cryoelectron microscopy ...
|READ MORE|
23-Apr-2013
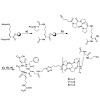
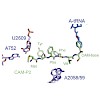
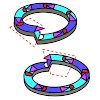
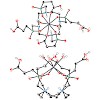
Jakub Šimeček, Petr Hermann, Jana Havlíčková, Eberhardt Herdtweck, Tobias G. Kapp, Nils Engelbogen, Horst Kessler, Hans-Jürgen Wester, Johannes Notni
Chemistry - A European Journal, 2013, DOI: 10.1002/chem.201300338, Volume 19, Issue 24, pages 7748–7757, published on 23.04.2013
Chemistry - A European Journal, online article
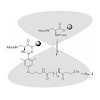
The cyclen-based tetraphosphinate chelator 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetrakis[methylene(2-carboxyethyl)phosphinic acid] (DOTPI) comprises four additional carboxylic acid moieties for bioconjugation. The thermodynamic stability constants (logKML) of metal complexes, as determined by potentiometry, were 23.11 for CuII, 20.0 for LuIII, 19.6 for YIII, ...
|READ MORE|
19-Apr-2013
Taner Cavlar, Tobias Deimling, Andrea Ablasser,
Karl-Peter Hopfner, Veit Hornung
The EMBO Journal,
2013,
doi:10.1038/emboj.2013.86, 32, 1440 - 1450 published on 19.04.2013
EMBO,
online article
Extensive research on antiviral small molecules starting in the early 1970s has led to the identification of 10-carboxymethyl-9-acridanone (CMA) as a potent type I interferon (IFN) inducer. Up to date, the mode of action of this antiviral molecule has remained elusive. Here we demonstrate that CMA mediates a cell-intrinsic type I IFN response, depending on the ...
|READ MORE|
21-Mar-2013
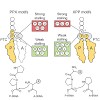
Tomas Jacso, Benjamin Bardiaux, Jana Broecker, Sebastian Fiedler, Tom Baerwinkel, Andi Mainz, Uwe Fink, Carolyn Vargas, Hartmut Oschkinat, Sandro Keller,
Bernd Reif J. Am. Chem. Soc.,,
2013,
DOI: 10.1021/ja408644f, 135 (50), pp 18884–18891 published on 21.03.2013
J. Am. Chem. Soc.,
online article
In vitro protein-folding studies using chemical denaturants such as urea are indispensible in elucidating the forces and mechanisms determining the stability, structure, and dynamics of water-soluble proteins. By contrast, α-helical membrane-associated proteins largely evade such approaches because they are resilient to extensive unfolding. We have used optical ...
|READ MORE|
19-Mar-2013
Martin Gräber, Michael Hell, Corinna Gröst, Anders Friberg, Bianca Sperl,
Michael Sattler, Thorsten Berg
Angewandte Chemie,
2013,
DOI: 10.1002/anie.201208889, 52,1-6, published on 19.03.2013
Angewandte Chemie, online article
Significant advances during the last decade in the field of small-molecule modulators of protein–protein interactions have raised general awareness of the fact that the modulation of protein–protein interactions has tremendous potential for both basic and applied science.[1] Some of the most advanced orthosteric inhibitors of protein–protein interactions[2–5] are ...
|READ MORE|
05-Mar-2013
Christopher J. Woolstenhulme, Shankar Parajuli, David W. Healey, Diana P. Valverde, E. Nicholas Petersen, Agata L. Starosta, Nicholas R. Guydosh, W. Evan Johnsoe,
Daniel N. Wilson, Allen R. Buskirk
PNAS,
2013,
www.pnas.org/cgi/doi/10.1073/pnas.1219536110, vol. 110 no. 10 published on 05.03.2013
PNAS,
online article
Although the ribosome is a very general catalyst, it cannot synthesize all protein sequences equally well. For example, ribosomes stall on the secretion monitor (SecM) leader peptide to regulate expression of a downstream gene. Using a genetic selection in Escherichia coli, we identified additional nascent peptide motifs that stall ribosomes. Kinetic studies show ...
|READ MORE|
03-Mar-2013
Janosch Hennig, Iren Wang, Miriam Sonntag, Frank Gabel,
Michael Sattler J Biomol NMR,
2013,
DOI 10.1007/s10858-013-9719-9, published on 03.03.2013
J Biomol NMR,
online article
Many processes in the regulation of gene expression and signaling involve the formation of protein complexes involving multi-domain proteins. Individual domains that mediate protein-protein and protein-nucleic acid interactions are typically connected by flexible linkers, which contribute to conformational dynamics and enable the formation of complexes with ...
|READ MORE|
22-Feb-2013
Carrie Bernecky,
Patrick Cramer The EMBO Journal,
2013,
doi:10.1038/emboj.2013.36, 32, 771 - 772 published on 22.02.2013
The EMBO Journal,
online article
In addition to its role in DNA-dependent transcription, RNA polymerase II (Pol II) possesses RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP) activity (Lehmann et al, 2007). In a study published in this issue of The EMBO Journal, Wagner et al (2013) report the first native cellular function of the RdRP activity of Pol II. The authors find that a mammalian non-coding RNA ...
|READ MORE|
19-Feb-2013
Lasse Jenner, Agata L. Starosta, Daniel S. Terry, Aleksandra Mikolajka, Liudmila Filonava Marat Yusupov, Scott C. Blanchard, Daniel N. Wilson, Gulnara Yusupova
PNAS, 2013, doi: 10.1073/pnas.1216691110, vol. 110 no. 10 3812-3816 published on 19.02.2013
PNAS, online article
Here we present an X-ray crystallography structure of the clinically relevant tigecycline antibiotic bound to the 70S ribosome. Our structural and biochemical analysis indicate that the enhanced potency of tigecycline results from a stacking interaction with nucleobase C1054 within the decoding site of the ribosome. Single-molecule fluorescence resonance energy ...
|READ MORE|
18-Feb-2013
Sam Asami, Magdalena Rakwalska-Bange, Teresa Carlomagno,
Bernd Reif Angewandte Chemie,
2013,
DOI: 10.1002/anie.201208024, Volume 52, Issue 8, pages 2345–2349, published on 18.02.2013
Angewandte Chemie,
online article
Both protonated and deuterated samples were employed in the study of the L7Ae box C/D RNA complex by 1H-detected solid-state NMR spectroscopy. This approach yielded high-resolution spectra and was used to determine the intermolecular interface and extract structural parameters with high accuracy.
|READ MORE|
18-Feb-2013
Divita Garg, Alexander V. Beribisky, Glauco Ponterini, Alessio Ligabue, Gaetano Marverti, Andrea Martello, M. Paola Costi , Michael Sattler, Rebecca C. Wade
Nucleic Acids Research, 2013, doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt098, 1–12 published on 18.02.2013
Nucleic Acids Research, online article
Resistance to drugs targeting human thymidylate synthase (TS) poses a major challenge in the field of anti-cancer therapeutics. Overexpression of the TS protein has been implicated as one of the factors leading to the development of resistance. Therefore, repressing translation by targeting the TS mRNA could help to overcome this problem. In this study, we report ...
|READ MORE|
15-Feb-2013
Benjamin Zeitler, Antonie Bernhard, Helge Meyer,
Michael Sattler, Hans-Ulrich Koop, Christian Lindermayr
Plant Mol Biol,
2013,
DOI 10.1007/s11103-012-9996-9, Volume 81, Issue 3, pp 259-272 published on 15.02.2013
Plant Mol Biol,
online article
Antimicrobial peptides are important defense compounds of higher organisms that can be used as therapeutic agents against bacterial and/or viral infections. We designed several antimicrobial peptides containing hydrophobic and positively charged clusters that are active against plant and human pathogens. Especially peptide SP1-1 is highly active with a MIC value ...
|READ MORE|
03-Feb-2013
Debora Lika Makino, Marc Baumgärtner,
Elena Conti Nature,
2013,
doi:10.1038/nature11870, 495, 70–75 published on 03.02.2013
Nature,
online article
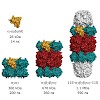
The exosome is the major 3′–5′ RNA-degradation complex in eukaryotes. The ubiquitous core of the yeast exosome (Exo-10) is formed by nine catalytically inert subunits (Exo-9) and a single active RNase, Rrp44. In the nucleus, the Exo-10 core recruits another nuclease, Rrp6. Here we crystallized an approximately 440-kilodalton complex of Saccharomyces cerevisiae ...
|READ MORE|
30-Jan-2013
Alexander Bochen, Udaya Kiran Marelli, Elke Otto, Diego Pallarola, Carlos Mas-Moruno, Francesco Saverio Di Leva, Heike Boehm, Joachim P. Spatz, Ettore Novellino,
Horst Kessler, Luciana Marinelli
J. Med. Chem.,
2013,
DOI: 10.1021/jm301221x, 56 (4), pp 1509–1519 published on 30.01.2013
J. Med. Chem.,
online article
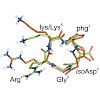
Integrins are the major class of cell adhesion proteins. Their interaction with different ligands of the extracellular matrix is diverse. To get more insight into these interactions, artificial ligands endowed with a well-defined activity/selectivity profile are necessary. Herein, we present a library of cyclic pentapeptides, based on our previously reported ...
|READ MORE|
28-Jan-2013
Florian Rechenmacher, Stefanie Neubauer, Julien Polleux, Carlos Mas-Moruno, Mariarosaria De Simone, Elisabetta Ada Cavalcanti-Adam, Joachim P. Spatz, Reinhard Fässler,
Horst Kessler,
Angewandte Chemie,
2013,
DOI: 10.1002/anie.201206370, Volume 52, Issue 5, pages 1572–1575 published on 23.04.2013
Angewandte Chemie,
online article
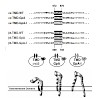
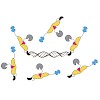
Stuck with the right choice: αvβ3- or α5β1-selective integrin ligands were functionalized for surface coating without losing activity and selectivity. The coating of nanostructured gold surfaces with these compounds stimulated subtype-selective cell adhesion of genetically modified αvβ3- or α5β1-expressing fibroblasts in vitro.
|READ MORE|
25-Jan-2013
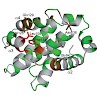
Fatiha Kateb, Helene Perrin, Konstantinos Tripsianes, Peijian Zou,Roberta Spadaccini, Matthew Bottomley, Titus M. Franzmann,
Johannes Buchner, Stephane Ansieau,
Michael Sattler Plos,
2013,
doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0054715, Volume 8, Issue 1, e54715 published on 25.01.2013
Plos, online article
DEAF-1 is an important transcriptional regulator that is required for embryonic development and is linked to clinical depression and suicidal behavior in humans. It comprises various structural domains, including a SAND domain that mediates DNA binding and a MYND domain, a cysteine-rich module organized in a Cys4-Cys2-His-Cys (C4-C2HC) tandem zinc binding motif. ...
|READ MORE|
17-Jan-2013
Carina Motz, Kerstin Monika Schuhmann, Axel Kirchhofer, Manuela Moldt, Gregor Witte, Karl-Klaus Conzelmann,
Karl-Peter Hopfner Science,
2013,
DOI: 10.1126/science.1230949, vol. 339 no. 6120 pp. 690-693 published on 17.01.2013
Science,
online article
The retinoic acid–inducible gene I (RIG-I)–like receptor (RLR) melanoma differentiation–associated protein 5 (MDA5) senses cytoplasmic viral RNA and activates antiviral innate immunity. To reveal how paramyxoviruses counteract this response, we determined the crystal structure of the MDA5 adenosine 5´-triphosphate (ATP)–hydrolysis domain in complex with the viral ...
|READ MORE|
14-Jan-2013
Sandrine Evellin, Federico Galvagni, Alessio Zippo, Francesco Neri, Maurizio Orlandini, Danny Incarnato, Daniela Dettori, Stefanie Neubauer,
Horst Kessler, Erwin F. Wagner, Salvatore Oliviero
Molecular and Cellular Biology,
2013,
doi: 10.1128/MCB.01054-12, published on 14.01.2013
Molecular and Cellular Biology,
online article
To form three-dimensional capillary tubes endothelial cells must establish contacts with the extracellular matrix that provides signals for their proliferation, migration, and differentiation. The transcription factor Fosl1 plays a key role in the vasculogenic and angiogenic processes, as Fosl1 knockout embryos die with vascular defects in extra-embryonic ...
|READ MORE|
09-Jan-2013
Marco Retzlaff, Julia Rohrberg, Natascha Jennifer Küpper, Stephan Lagleder, Alexander Bepperling, Florian Manzenrieder, Jirka Peschek,
Horst Kessler,
Johannes Buchner Journal of Molecular Biology,
2013,
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2012.10.015, Volume 425, Issue 1, Pages 144–155 published on 09.01.2013
Journal of Molecular Biology,
online article
The tumor suppressor protein p53 is often referred to as the guardian of the genome. In the past, controversial findings have been presented for the role of the C-terminal regulatory domain (RD) of p53 as both a negative regulator and a positive regulator of p53 activity. However, the underlying mechanism remained enigmatic. To understand the function of the RD ...
|READ MORE|