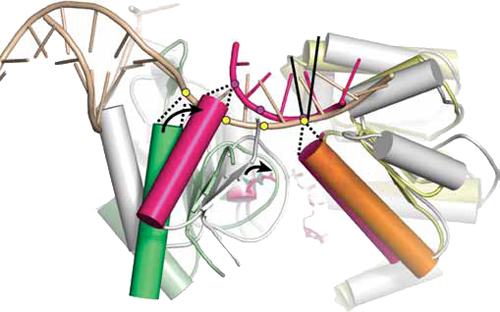
Structural basis for DNA duplex sepration by a superfamily-2 helicase
01-Jul-2007
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 2007, 14, 647-52 published on 01.07.2007
online article
To reveal the mechanism of processive strand separation by superfamily-2 (SF2) 3'-5' helicases, we determined apo and DNA-bound crystal structures of archaeal Hel308, a helicase that unwinds lagging strands and is related to human DNA polymerase h. Our structure captures the duplex-unwinding reaction, shows that initial strand separation does not require ATP and identifies a prominent beta-hairpin loop as the unwinding element. Similar loops in hepatitis C virus NS3 helicase and RNA-decay factors support the idea that this duplex-unwinding mechanism is applicable to a broad subset of SF2 helicases. Comparison with ATP-bound SF2 enzymes suggests that ATP promotes processive unwinding of 1 base pair by ratchet-like transport of the 3' product strand. Our results provide a first structural framework for strand separation by processive SF2 3'-5' helicases and reveal important mechanistic differences from SF1 helicases.