Structural basis for potent inhibitory activity of the antibiotic tigecycline during protein synthesis
19-Feb-2013
PNAS, 2013, doi: 10.1073/pnas.1216691110, vol. 110 no. 10 3812-3816 published on 19.02.2013
PNAS, online article
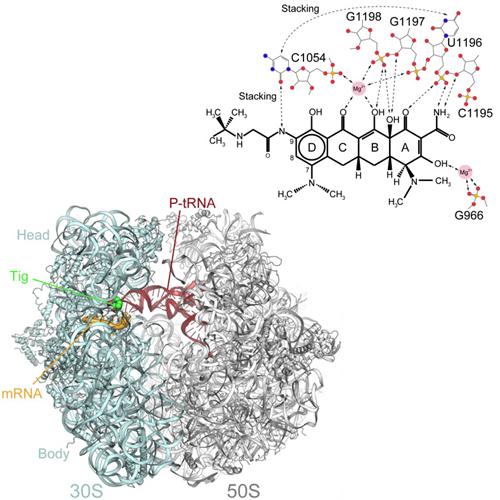
Here we present an X-ray crystallography structure of the clinically relevant tigecycline antibiotic bound to the 70S ribosome. Our structural and biochemical analysis indicate that the enhanced potency of tigecycline results from a stacking interaction with nucleobase C1054 within the decoding site of the ribosome. Single-molecule fluorescence resonance energy transfer studies reveal that, during decoding, tigecycline inhibits the initial codon recognition step of tRNA accommodation and prevents rescue by the tetracycline-resistance protein TetM.