Structural basis of transcription inhibition by alpha-amanitin and implications for RNA polymerase II translocation
13-Jun-2008
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 2011, doi:10.1038/nsmb.1458, 811-818 published on 13.06.2008
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, online article
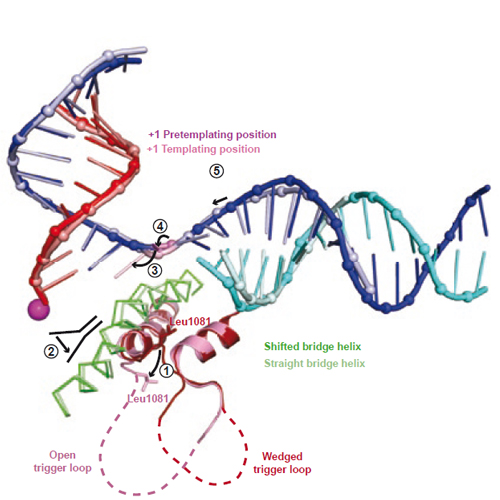
To study how RNA polymerase II translocates after nucleotide incorporation, we prepared elongation complex crystals in which pre- and post-translocation states interconvert. Crystal soaking with the inhibitor alpha-amanitin locked the elongation complex in a new state, which was refined at 3.4-Å resolution and identified as a possible translocation intermediate. The DNA base entering the active site occupies a 'pretemplating' position above the central bridge helix, which is shifted and occludes the templating position. A leucine residue in the trigger loop forms a wedge at the shifted bridge helix, but moves by 13 Å to close the active site during nucleotide incorporation. Our results support a Brownian ratchet mechanism that involves swinging of the trigger loop between open, wedged and closed positions, and suggest that alpha-amanitin impairs nucleotide incorporation and translocation by trapping the trigger loop and bridge helix.