Research Area D - Publications 2018
31-Dec-2018
Nature Chemical Biology, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-018-0194-1
Nature Chemical Biology, online article

Phosphorylation of the carboxyl-terminal domain (CTD) of the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) governs stage-specific interactions with different cellular machines. The CTD consists of Y1S2P3T4S5P6S7 heptad repeats and sequential phosphorylations of Ser7, Ser5 and Ser2 occur universally at Pol II-transcribed genes. Phosphorylation of Thr4, however, ...
22-Nov-2018
Nucleic Acids Research, 2018, 1, doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1148
Nucleic Acids Research, online article
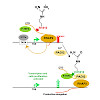
Mammalian-wide interspersed repeats (MIRs) are retrotransposed elements of mammalian genomes. Here, we report the specific binding of zinc finger protein ZNF768 to the sequence motif GCTGTGTG (N20) CCTCTCTG in the core region of MIRs. ZNF768 binding is preferentially associated with euchromatin and promoter regions of genes. Binding was observed for genes ...
21-Nov-2018
Molecular Cell, 73, 1–13, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2018.10.016
Molecular Cell, online article
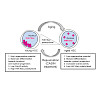
The post-translational modification of key residues at the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II (RNAP2-CTD) coordinates transcription, splicing, and RNA processing by modulating its capacity to act as a landing platform for a variety of protein complexes. Here, we identify a new modification at the CTD, the deimination of arginine and its conversion to ...
07-Nov-2018
Genome Biology 2018, 19:189, https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-018-1557-3
Genome Biology, online article
Background
The decline of hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) function upon aging contributes to aging-associated immune remodeling and leukemia pathogenesis. Aged HSCs show changes to their epigenome, such as alterations in DNA methylation and histone methylation and acetylation landscapes. We previously showed a correlation between high Cdc42 activity in aged HSCs ...
01-Nov-2018
Molecular Cell 72, 1–12, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2018.09.032
Molecular Cell, online article
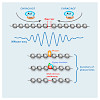
Regular successions of positioned nucleosomes, or phased nucleosome arrays (PNAs), are predominantly known from transcriptional start sites (TSSs). It is unclear whether PNAs occur elsewhere in the genome. To generate a comprehensive inventory of PNAs for Drosophila, we applied spectral analysis to nucleosome maps and identified thousands of PNAs throughout the ...
17-Oct-2018
Nature, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0619-8
Nature, online article

Many evolutionarily distant pathogenic organisms have evolved similar survival strategies to evade the immune responses of their hosts. These include antigenic variation, through which an infecting organism prevents clearance by periodically altering the identity of proteins that are visible to the immune system of the host. Antigenic variation requires large ...
03-Sep-2018
EMBO reports (2018), Volume 19, Issue 10 , DOI 10.15252/embr.201744445
EMBO reports, online article
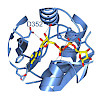
MacroH2A histone variants suppress tumor progression and act as epigenetic barriers to induced pluripotency. How they impart their influence on chromatin plasticity is not well understood. Here, we analyze how the different domains of macroH2A proteins contribute to chromatin structure and dynamics. By solving the crystal structure of the macrodomain of human ...
20-Aug-2018
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology; https://doi.org/10.1038/s41594-018-0110-0
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, online article

The nature of chromatin as regular succession of nucleosomes has gained iconic status. However, since most nucleosomes in metazoans are poorly positioned it is unknown to which extent bulk genomic nucleosome repeat length reflects the regularity and spacing of nucleosome arrays at individual loci. We describe a new approach to map nucleosome array regularity and ...
25-Jul-2018
Epigenetics & Chromatin 2018, 11:41, https://doi.org/10.1186/s13072-018-0211-3
Epigenetics & Chromatin, online article

Background
Epigenome-wide association studies (EWAS) based on human brain samples allow a deep and direct understanding of epigenetic dysregulation in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). However, strong variation of cell-type proportions across brain tissue samples represents a significant source of data noise. Here, we report the first EWAS based on sorted neuronal and ...
28-Jun-2018
PLoS ONE, 13(6): e0199782, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0199782
PLoS ONE, online article
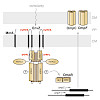
Although distinct amino acid motifs containing consecutive prolines (polyP) cause ribosome stalling, which necessitates recruitment of the translation elongation factor P (EF-P), they occur strikingly often in bacterial proteomes. For example, polyP motifs are found in more than half of all histidine kinases in Escherichia coli K-12, which raises the question of ...
11-Jun-2018
Scientific Reports, volume 8, Article number: 8810 (2018), https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-27125-6
Scientific Reports, online article
Checkpoint molecules such as programmed death 1 (PD-1) dampen excessive T cell activation to preserve immune homeostasis. PD-1-specific monoclonal antibodies have revolutionized cancer therapy, as they reverse tumour-induced T cell exhaustion and restore CTL activity. Based on this success, deciphering underlying mechanisms of PD-1-mediated immune functions has ...
25-Apr-2018
Open Biol., 8: 180023, http://dx.doi.org/10.1098/rsob.180023
Open Biol., online article
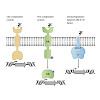
Every living cell possesses numerous transmembrane signalling systems that receive chemical and physical stimuli from the environment and transduce this information into an intracellular signal that triggers some form of cellular response. As unicellular organisms, bacteria require these systems for survival in rapidly changing environments. The receptors ...
19-Mar-2018
J. Bacteriol., vol. 200 no. 15 e00740-17, doi: 10.1128/JB.00740-17
J. Bacteriol., online article
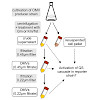
Many bacteria use extracellular signaling molecules to coordinate group behavior, a process referred to as quorum sensing (QS). However, some QS molecules are hydrophobic in character and are probably unable to diffuse across the bacterial cell envelope. How these molecules are disseminated between bacterial cells within a population is not yet fully understood. ...
08-Mar-2018
JCI Insight. 2018;3(5):e96322. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.96322
JCI Insight., online article
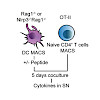
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is associated with enhanced levels of the IL-1 family cytokines IL-1β and IL-18, which are activated by the Nlrp3 inflammasome. Here, we investigated the role of inflammasome-driven cytokine release on T cell polarization and DC differentiation in steady state and T cell transfer colitis. In vitro and in vivo data showed that ...
09-Feb-2018
Life Science Alliance, Volume 1, No. 1, DOI: 10.26508/lsa.201800024
Life Science Alliance, online article
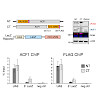
The chromatin remodeling complexes chromatin accessibility complex and ATP-utilizing chromatin assembly and remodeling factor (ACF) combine the ATPase ISWI with the signature subunit ACF1. These enzymes catalyze well-studied nucleosome sliding reactions in vitro, but how their actions affect physiological gene expression remains unclear. Here, we explored the ...
01-Feb-2018
PLoS Comput Biol., 14(2), e1005987. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005987
PLoS Comput Biol., online article
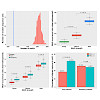
Translation of consecutive prolines causes ribosome stalling, which is alleviated but cannot be fully compensated by the elongation factor P. However, the presence of polyproline motifs in about one third of the E. coli proteins underlines their potential functional importance, which remains largely unexplored. We conducted an evolutionary analysis of polyproline ...
31-Jan-2018
Molecular Metabolism, Volume 9, March 2018, Pages 57-68, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2018.01.011
Molecular Metabolism, online article
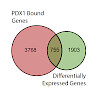
Objective: Homozygous loss-of-function mutations in the gene coding for the homeobox transcription factor (TF) PDX1 leads to pancreatic agenesis, whereas heterozygous mutations can cause Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young 4 (MODY4). Although the function of Pdx1 is well studied in pre-clinical models during insulin-producing β-cell development and homeostasis, ...
31-Jan-2018
Mitochondrion, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mito.2018.01.005
Mitochondrion, online ablage
Mitochondrial localized proteins are mostly synthesized in the cytosol and translocated across the outer mitochondrial membrane via the translocase of the outer membrane (TOM) complex. Although the channel protein is conserved among eukaryotes, the receptor proteins are more divergent and show features specific to the plant lineage. OM64, which is a paralogue of ...
19-Jan-2018
Science, Vol. 359, Issue 6373, eaan1133, DOI: 10.1126/science.aan1133
Science, online article
Classical structural biology can only provide static snapshots of biomacromolecules. Single-molecule Förster resonance energy transfer (smFRET) paved the way for studying dynamics in macromolecular structures under biologically relevant conditions. Since its first implementation in 1996, smFRET experiments have confirmed previously hypothesized mechanisms and ...
19-Jan-2018
Nature Communications, 9, Article number: 299, doi:10.1038/s41467-017-02582-1
Nature Communications, online article

The ubiquitously expressed RNA-binding proteins Roquin-1 and Roquin-2 are essential for appropriate immune cell function and postnatal survival of mice. Roquin proteins repress target mRNAs by recognizing secondary structures in their 3′-UTRs and by inducing mRNA decay. However, it is unknown if other cellular proteins contribute to target control. To identify ...
09-Jan-2018
eLife 2018;7:e32010 doi: 10.7554/eLife.32010
eLife, online article

The transcription factor c-Myc amplifies the transcription of many growth-related genes in cancer cells, but its role as an oncogene is not fully understood.
04-Jan-2018
Molecular Cell, 69, 48–61, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2017.12.009
Molecular Cell, online article
The carboxy-terminal domain (CTD) of RNA polymerase (Pol) II is composed of a repetition of YSPTSPS heptads and functions as a loading platform for protein complexes that regulate transcription, splicing, and maturation of RNAs. Here, we studied mammalian CTD mutants to analyze the function of tyrosine1 residues in the transcription cycle. Mutation of 3/4 of the ...
17-Sep-2017
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., Volume 57, Issue 9, Pages 2314-2333, https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201708459
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., online article
Nanobodies can be seen as next‐generation tools for the recognition and modulation of antigens that are inaccessible to conventional antibodies. Due to their compact structure and high stability, nanobodies see frequent usage in basic research, and their chemical functionalization opens the way towards promising diagnostic and therapeutic applications. In this ...