CTD serine-2 plays a critical role in splicing and termination factor recruitment to RNA polymerase II in vivo
28-Dec-2012
Nucleic Acids Research, 2012, doi:10.1093/nar/gks1327, 1–13 published on 28.12.2012
Nucleic Acids Research, online article
Nucleic Acids Research, online article
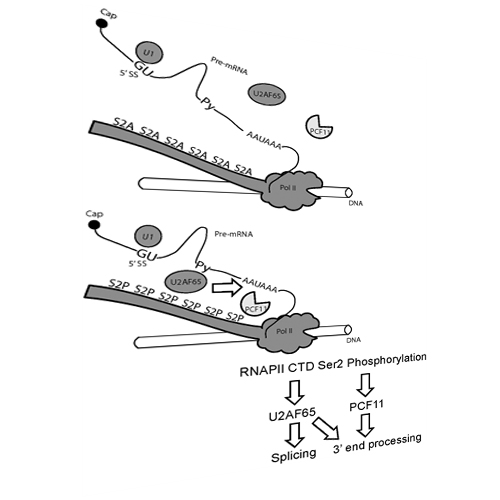
Co-transcriptional pre-mRNA processing relies on reversible phosphorylation of the carboxyl-terminal domain (CTD) of Rpb1, the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II (RNAP II). In this study, we replaced in live cells the endogenous Rpb1 by S2A Rpb1, where the second serines (Ser2) in the CTD heptapeptide repeats were switched to alanines, to prevent phosphorylation. Although slower, S2A RNAP II was able to transcribe. However, it failed to recruit splicing components such as U2AF65 and U2 snRNA to transcription sites, although the recruitment of U1 snRNA was not affected. As a consequence, co-transcriptional splicing was impaired. Interestingly, the magnitude of the S2A RNAP II splicing defect was promoter dependent. In addition, S2A RNAP II showed an impaired recruitment of the cleavage factor PCF11 to pre-mRNA and a defect in 3′-end RNA cleavage. These results suggest that CTD Ser2 plays critical roles in co-transcriptional pre-mRNA maturation in vivo: It likely recruits U2AF65 to ensure an efficient co-transcriptional splicing and facilitates the recruitment of pre-mRNA 3′-end processing factors to enhance 3′-end cleavage.