The Activation Potential of MOF Is Constrained for Dosage Compensation
25-Jun-2010
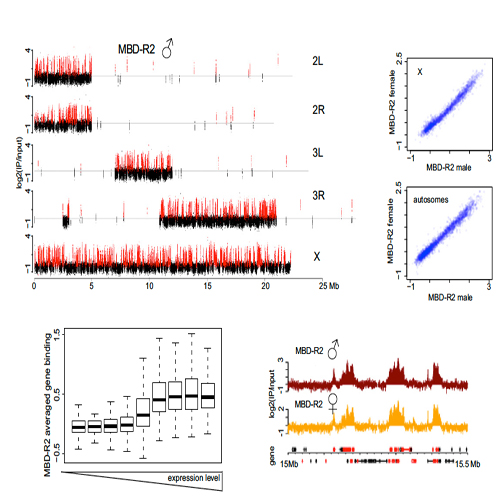
The H4K16 acetyltransferase MOF plays a crucial role in dosage compensation in Drosophila but has additional, global functions. We compared the molecular context and effect of MOF in male and female flies, combining chromosome-wide mapping and transcriptome studies with analyses of defined reporter loci in transgenic flies. MOF distributes dynamically between two complexes, the dosage compensation complex and a complex containing MBD-R2, a global facilitator of transcription. These different targeting principles define the distribution of MOF between the X chromosome and autosomes and at transcription units with 50 or 30 enrichment. The male X chromosome differs from all other chromosomes in that H4K16 acetylation levels do not correlate with transcription output. The reconstitution of this phenomenon at a model locus revealed that the activation potential of MOF is constrained in male cells in the context of the DCC to arrive at the 2-fold activation of transcription characteristic of dosage compensation.