Research Area A - Publications 2013
24-Dec-2013
PNAS, online article
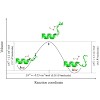
Volume changes associated with protein folding reactions contain valuable information about the folding mechanism and the nature of the transition state. However, meaningful interpretation of such data requires that overall volume changes be deconvoluted into individual contributions from different structural components. Here we focus on one type of structural ...
20-Dec-2013
Chemistry, online article
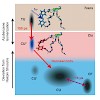
Conformational changes in proteins and peptides can be initiated by diverse processes. This raises the question how the variation of initiation mechanisms is connected to differences in folding or unfolding processes. In this work structural dynamics of a photoswitchable β-hairpin model peptide were initiated by two different mechanisms: temperature jump (T-jump) ...
17-Dec-2013
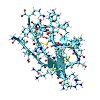
The structural sensitivity of NMR chemical shifts as computed by quantum chemical methods is compared to a variety of empirical approaches for the example of a prototypical peptide, the 38-residue kaliotoxin KTX comprising 573 atoms. Despite the simplicity of empirical chemical shift prediction programs, the agreement with experimental results is rather good, ...
03-Oct-2013
Chemistry of Materials, online article
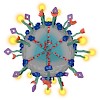
Nanosized mesoporous silica particles with high colloidal stability attract growing attention as drug delivery systems for targeted cancer treatment and as bioimaging devices. This Perspective describes recent breakthroughs in mesoporous silica nanoparticle design to demonstrate their high potential as multifunctional drug delivery nanocarriers. These types of ...
10-Sep-2013
J. Am. Chem. Soc., online article

The CH3 homodimer at the C-terminal end of the antibody heavy chain is the key noncovalent interaction stabilizing antibody proteins. Here, we use single-molecule force spectroscopy to investigate the dissociation mechanics of CH3 as a proxy for antibody mechanical stability. We find the CH3 homodimer to be a highly stable complex, and its dissociation force of ...
27-Aug-2013
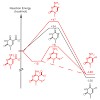
Three new cytosine derived DNA modifications, 5-hydroxymethyl-2′-deoxycytidine (hmdC), 5-formyl-2′-deoxycytidine (fdC) and 5-carboxy-2′-deoxycytidine (cadC) were recently discovered in mammalian DNA, particularly in stem cell DNA. Their function is currently not clear, but it is assumed that in stem cells they might be intermediates of an active demethylation ...
06-Aug-2013
PNAS, online article
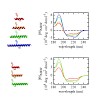
The dynamics of peptide α-helices have been studied extensively for many years, and the kinetic mechanism of the helix–coil dynamics has been discussed controversially. Recent experimental results have suggested that equilibrium helix–coil dynamics are governed by movement of the helix/coil boundary along the peptide chain, which leads to slower unfolding ...
02-Jul-2013
Z. Naturforsch., online article
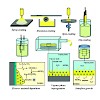
In this article, we discuss how fluorescence microscopy techniques are used to investigate important characteristics of porous silica materials. We start with a discussion of the synthesis, formation mechanism and functionalization of these materials. We then give an introduction to single molecule microscopy and show how this technique can be used to gain deeper ...
30-Jun-2013
Methods in Enzymology, online article
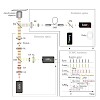
Pulsed interleaved excitation (PIE) is the methodology of interleaved or alternating excitation of different fluorophores on the nanosecond timescale, which allows quasi-simultaneous, yet independent measurements to be performed. PIE simplifies quantification of several fluorescence techniques such as FCCS and FRET experiments. Foremost, it allows to specifically ...
21-Jun-2013
Angewandte Chemie, online article
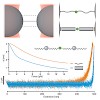
Single molecule mechanical techniques like AFM or optical tweezers provide insight into the conformational dynamics of macromolecules and allow reconstructing details of the free energy landscapes that direct such processes.1 Single-molecule mechanical assays have been successfully applied to analyze large conformational changes like the ones that occur in ...
10-Jun-2013
J. Org. Chem., online article
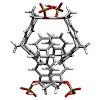
Selective binding of the phosphate-substituted molecular tweezer 1a to protein lysine residues was suggested to explain the inhibition of certain enzymes and the aberrant aggregation of amyloid petide Aβ42 or α-synuclein, which are assumed to be responsible for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease, respectively. In this work we systematically investigated the ...
04-Jun-2013
Biophysical Journal, online article
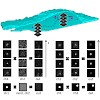
The interactions and coordination of biomolecules are crucial for most cellular functions. The observation of protein interactions in live cells may provide a better understanding of the underlying mechanisms. After fluorescent labeling of the interacting partners and live-cell microscopy, the colocalization is generally analyzed by quantitative global methods. ...
17-May-2013
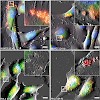
In this study, it is shown that the cytotoxic response of cells as well as the uptake kinetics of nanoparticles (NPs) is cell type dependent. We use silica NPs with a diameter of 310 nm labeled with perylene dye and 304 nm unlabeled particles to evaluate cell type-dependent uptake and cytotoxicity on human vascular endothelial cells (HUVEC) and cancer cells ...
Targeted Drug Delivery in Cancer Cells with Red-Light Photoactivated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles
13-May-2013
Mesoporous nanoparticles for drug delivery would benefit significantly from further improvements in targeting efficiency and endosomal release. We present a system based on colloidal mesoporous silica nanoparticles with targeting-ligands and a red-light photosensitizer. This nanoparticle system provides spatial and temporal control of the release of drugs into ...
10-May-2013
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., online article
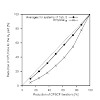
The calculation of molecular response properties in dynamic molecular systems is a major challenge that requires sampling over many steps of, e.g., Born–Oppenheimer molecular dynamics (BO-MD) simulations. We present an extrapolation scheme to accelerate such calculations for multiple steps within BO-MD trajectories or equivalently within other sampling methods of ...
01-May-2013
J. Chem. Phys., online article
An atomic-orbital (AO) based formulation for calculating nuclear magnetic resonance chemical shieldings at the second-order Møller-Plesset perturbation theory level is introduced, which provides a basis for reducing the scaling of the computational effort with the molecular size from the fifth power to linear and for a specific nucleus to sublinear. The latter ...
26-Apr-2013
The EMBO Journal, online article
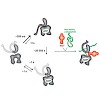
The numerous functions of the important class of molecular chaperones, heat shock proteins 70 (Hsp70), rely on cycles of intricate conformational changes driven by ATP-hydrolysis and regulated by cochaperones and substrates. Here, we used Förster resonance energy transfer to study the conformational dynamics of individual molecules of Ssc1, a mitochondrial Hsp70, ...
19-Apr-2013
Acta Neuropathol, 2013, DOI: 10.1007/s00401-013-1114-9, 795-813 published on 19.04.2013
Acta Neuropathol, online article
In neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Parkinson’s disease (PD) and prion diseases, deposits of aggregated disease-specific proteins are found. Oligomeric aggregates are presumed to be the key neurotoxic agent. Here we describe the novel oligomer modulator anle138b [3-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-5-(3-bromophenyl)-1H-pyrazole], an aggregation ...
04-Apr-2013
J. Chem. Phys., online article
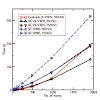
We present a simple but accurate preselection method based on Schwarz integral estimates to determine the significant elements of the exact exchange matrix before its evaluation, thus providing an asymptotical linear-scaling behavior for non-metallic systems. Our screening procedure proves to be highly suitable for exchange matrix calculations on massively ...
13-Mar-2013
The Journal of Biological Chemistry, online article
The actin cytoskeleton is a central mediator of cellular morphogenesis, and rapid actin reorganization drives essential processes such as cell migration and cell division. Whereas several actin-binding proteins are known to be regulated by changes in intracellular pH, detailed information regarding the effect of pH on the actin dynamics itself is still lacking. ...
10-Mar-2013
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, online article
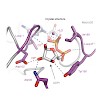
ADP-ribosylation is a reversible post-translational modification with wide-ranging biological functions in all kingdoms of life. A variety of enzymes use NAD+ to transfer either single or multiple ADP-ribose (ADPr) moieties onto distinct amino acid substrates, often in response to DNA damage or other stresses. Poly-ADPr-glycohydrolase readily reverses ...
05-Feb-2013
Nanomedicine, online article
This study examines the absolute quantification of particle uptake into cells. Methods: We developed a novel method to analyze stacks of confocal fluorescence images of single cells interacting with nano- and micro-particles. Particle_in_Cell-3D is a freely available ImageJ macro. During the image analysis routine, single cells are reconstructed in 3D and split ...
04-Feb-2013
Structural Biology, online article

Force spectroscopy has developed into an indispensable tool for studying folding and binding of proteins on a single molecule level in real time. Design of the pulling geometry allows tuning the reaction coordinate in a very precise manner. Many recent experiments have taken advantage of this possibility and have provided detailed insight the folding pathways on ...
19-Jan-2013
Peptide Science, 2013, DOI: 10.1002/bip.22171, Volume 100, Issue 1, pages 38–50 published on 19.01.2013
Peptide science, online article
The intramolecular and intermolecular vibrational energy flow in a polyproline peptide with a total number of nine amino acids in the solvent dimethyl sulfoxide is investigated using time-resolved infrared (IR) spectroscopy. Azobenzene covalently bound to a proline sequence containing nitrophenylalanine as a local sensor for vibrational excess energy serves as a ...










