Research Area A - Publications 2018
26-Oct-2018
PNAS, vol. 115, no. 46, 11688–11693, www.pnas.org/cgi/doi/10.1073/pnas.1807618115
PNAS, online article
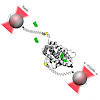
The glucocorticoid receptor (GR) is a prominent nuclear receptor linked to a variety of diseases and an important drug target. Binding of hormone to its ligand binding domain (GR-LBD) is the key activation step to induce signaling. This process is tightly regulated by the molecular chaperones Hsp70 and Hsp90 in vivo. Despite its importance, little is known about ...
18-Sep-2018
J. Biol. Chem. (2018) 293(44) 17107–17118, DOI 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005475
J. Biol. Chem., online article
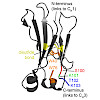
Despite their importance for antibody architecture and design, the principles governing antibody domain stability are still not understood in sufficient detail. Here, to address this question, we chose a domain from the invariant part of IgG, the CH2 domain. We found that compared with other Ig domains, the isolated CH2 domain is a surprisingly unstable monomer, ...
31-Aug-2018
Nature Methods, VOL 15, 669–676, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-018-0085-0
Nature Methods, online article

Single-molecule Förster resonance energy transfer (smFRET) is increasingly being used to determine distances, structures, and dynamics of biomolecules in vitro and in vivo. However, generalized protocols and FRET standards to ensure the reproducibility and accuracy of measurements of FRET efficiencies are currently lacking. Here we report the results of a ...
18-Jul-2018
Nanoscale, 2018, 10, 16416, DOI: 10.1039/c8nr03361g
Nanoscale, online article
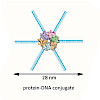
Fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) has been instrumental to determine the structure and dynamics of biomolecules but distances above 8 nanometer are not accessible. However, with the advent and rapid development of super-resolution (SR) microscopy, distances between two fluorescent dyes below 20 nanometer can be resolved, which hitherto has been ...
11-May-2018
J. Phys. Chem. A, 2018, 122 (21), pp 4819–4828, DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpca.8b02050
J. Phys. Chem. A, online article
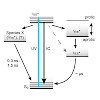
The decay of electronically excited states of thymine (Thy) and thymidine 5′-monophosphate (TMP) was studied by time-resolved UV/vis and IR spectroscopy. In addition to the well-established ultrafast internal conversion to the ground state, a so far unidentified UV-induced species is observed. In D2O, this species decays with a time constant of 300 ps for thymine ...
04-May-2018
Nature Communications, volume 9, Article number: 1806 (2018), https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-04139-2
Nature Communications, online article

Pore-forming toxins (PFT) are virulence factors that transform from soluble to membrane-bound states. The Yersinia YaxAB system represents a family of binary α-PFTs with orthologues in human, insect, and plant pathogens, with unknown structures. YaxAB was shown to be cytotoxic and likely involved in pathogenesis, though the molecular basis for its two-component ...
PAM: A Framework for Integrated Analysis of Imaging, Single-Molecule, and Ensemble Fluorescence Data
10-Apr-2018
Biophysical Journal, Volume 114, Issue 7, Pages 1518-1528, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2018.02.035
Biophysical Journal, online article
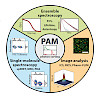
Fluorescence microscopy and spectroscopy data hold a wealth of information on the investigated molecules, structures, or organisms. Nowadays, the same fluorescence data set can be analyzed in many ways to extract different properties of the measured sample. Yet, doing so remains slow and cumbersome, often requiring incompatible software packages. Here, we present ...
22-Feb-2018
Methods, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2018.01.022
Methods, online article
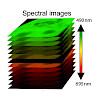
Raster image cross-correlation spectroscopy (ccRICS) can be used to quantify the interaction affinities between diffusing molecules by analyzing the fluctuations between two-color confocal images. Spectral crosstalk compromises the quantitative analysis of ccRICS experiments, limiting multicolor implementations to dyes with well-separated emission spectra. Here, ...
14-Feb-2018
bioRxiv, doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/265405
bioRxiv, online article
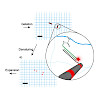
Expansion microscopy evolved as an interesting alternative in the field of super-resolution microscopy by physically expanding the target sample to increase its size by a multiple and to subsequently image the sample by conventional fluorescence microcopy. But the quantitative determination of the expansion factor remains challenging, since microscopic ...
12-Feb-2018
Nano Lett., 2018, 18 (3), pp 1962–1971, DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.7b05354
Nano Lett., online article

We explore the potential of DNA nanotechnology for developing novel optical voltage sensing nano-devices that convert a local change of electric potential into optical signals. As a proof-of-concept of the sensing mechanism, we assembled voltage responsive DNA origami structures labelled with a single pair of FRET dyes. The DNA structures were reversibly ...
06-Feb-2018
Chemical Physics, 512 (2018) 116–121, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemphys.2018.02.003
Chemical Physics, online article
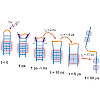
The light triggered unfolding reaction of the azobenzene peptide AzoTrpZip2 is investigated from 1 ps to 100 µs. Absorption changes show that the unfolding is a multistep process with the initial breaking of the hydrogen bonds in the vicinity of the AMPP chromophore on the 1 ns time scale followed by the disappearance of the remaining interstrand hydrogen bonds ...
02-Feb-2018
ChemBioChem, 9(8) (2018, 780–783, DOI: 10.1002/cbic.201700696
ChemBioChem, online article
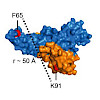
Human cells are complex entities in which molecular recognition and selection are critical for cellular processes often driven by structural changes and dynamic interactions. Biomolecules appear in different chemical states and modifications like phosphorylation affect their function. Hence, using proteins in their chemically native state in biochemical and ...
19-Jan-2018
Science, Vol. 359, Issue 6373, pp. 296-301, DOI: 10.1126/science.aao4284
Science, online article
The use of dynamic, self-assembled DNA nanostructures in the context of nanorobotics requires fast and reliable actuation mechanisms. We therefore created a 55-nanometer–by–55-nanometer DNA-based molecular platform with an integrated robotic arm of length 25 nanometers, which can be extended to more than 400 nanometers and actuated with externally applied ...
15-Jan-2018
Nature Chemistry, doi:10.1038/nchem.2916
Nature Chemitry, online article
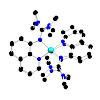
The entatic state denotes a distorted coordination geometry of a complex from its typical arrangement that generates an improvement to its function. The entatic-state principle has been observed to apply to copper electron-transfer proteins and it results in a lowering of the reorganization energy of the electron-transfer process. It is thus crucial for a ...
05-Jan-2018
BioEssays 2018, 1700078, Volume40, Issue3, DOI: 10.1002/bies.201700078
BioEssays, online article
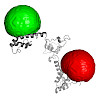
Conformational changes of proteins and other biomolecules play a fundamental role in their functional mechanism. Single pair Förster resonance energy transfer (spFRET) offers the possibility to detect these conformational changes and dynamics, and to characterize their underlying kinetics. Using spFRET on microscopes with different modes of detection, dynamic ...
01-Jan-1970
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, volume 25, 90–100 (2018), doi:10.1038/s41594-017-0012-6
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, online article
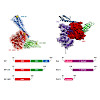
BiP is the endoplasmic member of the Hsp70 family. BiP is regulated by several co-chaperones including the nucleotide-exchange factor (NEF) Bap (Sil1 in yeast). Bap is a two-domain protein. The interaction of the Bap C-terminal domain with the BiP ATPase domain is sufficient for its weak NEF activity. However, stimulation of the BiP ATPase activity requires ...










