Research Area B - Publications 2010
29-Dec-2010
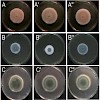
The mannosyltransferase Och1 is the key enzyme for synthesis of elaborated protein N-glycans in yeast. In filamentous fungi genes implicated in outer chain formation are present, but their function is unclear. In this study we have analyzed the Och1 protein of Aspergillus fumigatus. We provide first evidence that poly-mannosylated N-glycans exist in A. fumigatus ...
19-Dec-2010
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, online article
The chaperone cycle of heat shock protein-90 (Hsp90) involves progression through defined complexes with different cochaperones. It is still enigmatic how the exchange of cochaperones is regulated. The first cochaperone entering the cycle is the Hsp90 ATPase inhibitor Sti1 (Hop in human), which later is replaced by a prolyl isomerase (PPIase) and p23. We found, ...
09-Nov-2010
PNAS, 2010, doi: 10.1073/pnas.1009124107, vol. 107 no. 45 19260-19265 published on 09.11.2010
PNAS, online article

Ferredoxin:NADPH oxidoreductase (FNR) is a key enzyme of photosynthetic electron transport required for generation of reduction equivalents. Recently, two proteins were found to be involved in membrane-anchoring of FNR by specific interaction via a conserved Ser/Pro-rich motif: Tic62 and Trol. Our crystallographic study reveals that the FNR-binding motif, which ...
22-Oct-2010
Molecular Cell, online article
Organisms must survive a variety of stressful conditions, including sudden temperature increases that damage important cellular structures and interfere with essential functions. In response to heat stress, cells activate an ancient signaling pathway leading to the transient expression of heat shock or heat stress proteins (Hsps). Hsps exhibit sophisticated ...
02-Oct-2010
Biochimica et Piophysica Acta, online article
Chloroplasts originated from an endosymbiotic event, in which an ancestral photosynthetic cyanobacterium was engulfed by a mitochondriate eukaryotic host cell. During evolution, the endosymbiont lost its autonomy by means of a massive transfer of genetic information from the prokaryotic genome to the host nucleus. Consequently, the development of protein import ...
27-Aug-2010
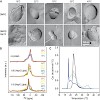
Hsp12 of S. cerevisiae is upregulated several 100-fold in response to stress. Our phenotypic analysis showed that this protein is important for survival of a variety of stress conditions, including high temperature. In the absence of Hsp12, we observed changes in cell morphology under stress conditions. Surprisingly, in the cell, Hsp12 exists both as a soluble ...
26-Aug-2010
Genome Biology, 2010, doi:10.1186/gb-2010-11-8-216, published on 26.08.2010
Genome Biology, online article
Diploid genomes are exquisitely balanced systems of gene expression. The dosage-compensation systems that evolved along with monosomic sex chromosomes exemplify the intricacies of compensating for differences in gene copy number by transcriptional regulation.
24-Aug-2010

The molecular chaperone heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) is an important and abundant protein in eukaryotic cells, essential for the activation of a large set of signal transduction and regulatory proteins. During the functional cycle, the Hsp90 dimer performs large conformational rearrangements. The transient N-terminal dimerization of Hsp90 has been extensively ...
23-Aug-2010
JCB, online article

Ribosomes arranged in pairs (100S) have been related with nutritional stress response and are believed to represent a “hibernation state.” Several proteins have been identified that are associated with 100S ribosomes but their spatial organization has hitherto not been characterized. We have used cryoelectron tomography to reveal the three-dimensional ...
18-Aug-2010
Trends in Plant Science, online article

During the evolution of photosynthesis, regulatory circuits were established that allow the precise coupling of light-driven electron transfer chains with downstream processes such as carbon fixation. The ferredoxin (Fd):ferredoxin–NADP+ oxidoreductase (FNR) couple is an important mediator for these processes because it provides the transition from exclusively ...
03-Aug-2010
Trends in Plant Science, online article
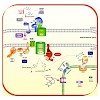
The import of chloroplast proteins synthesized in the cytosol of a plant cell is mediated by two multiprotein complexes or translocons located at the outer and inner membranes of the chloroplast envelope, respectively, TOC and TIC. These complexes integrate different signals to assure the timely transport of proteins into the chloroplast in accordance with the ...
30-Jul-2010
Journal of Molecular Biology, online article

In biological systems, proteins rarely act as isolated monomers. Association to dimers or higher oligomers is a commonly observed phenomenon. As an example, small heat shock proteins form spherical homo-oligomers of mostly 24 subunits, with the dimeric αlpha-crystallin domain as the basic structural unit. The structural hierarchy of this complex is key to its ...
17-Jul-2010
Microbes and Infection, online article
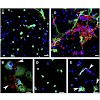
Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) represent a distinct mechanism to control and eliminate microbial infections. Our results show that conidia and germ tubes of the human pathogenic mold Aspergillus fumigatus are able to trigger the formation of NETs. Viable fungal cells are not essentially required for this hostepathogen interaction. Neutrophils engulf ...
09-Jul-2010
Cell, 2010, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.05.027, Volume 142, Issue 1, 112-122 published on 09.07.2010
Cell, online article
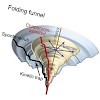
GroEL and GroES form a chaperonin nano-cage for single protein molecules to fold in isolation. The folding properties that render a protein chaperonin dependent are not yet understood. Here, we address this question using a double mutant of the maltosebinding protein DM-MBP as a substrate. Upon spontaneous refolding, DM-MBP populates a kinetically trapped ...
25-Jun-2010
Journal of Molecular Biology, online article
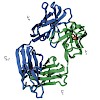
Intact antibodies and antigen binding fragments (Fab) have been previously shown to form an alternatively folded state (AFS) at low pH. This state consists primarily of secondary structure interactions, with reduced tertiary structure content. The AFS can be distinguished from the molten globule state by the formation of nonnative structure and, in particular, ...
21-Jun-2010
Plant Biology, online article
The membrane proteins of the plant preprotein and amino acid transporter (PRAT) superfamily all share common structural elements, such as four membrane-spanning α-helices. Interestingly they display diverse localisation to outer and inner membranes of chloroplasts and mitochondria. Furthermore, they fulfil different functions in preprotein translocation as well ...
15-Jun-2010
JMB, online article
Rhomboids are a family of intramembrane serine proteases that are conserved in bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes. They are required for numerous fundamental cellular functions such as quorum sensing, cell signaling, and mitochondrial dynamics. Mitochondrial rhomboids form an evolutionarily distinct class of rhomboids. It is largely unclear how their activity is ...
25-May-2010
The FASEB Journal, online article

Small heat shock proteins (sHsps) are molecular chaperones involved in maintaining protein homeostasis; they have also been implicated in protein folding diseases and in cancer. In this protein family, a conserved core domain, the so-called alpha-crystallin or Hsp20 domain, is flanked by highly variable, nonconserved sequences that are essential for chaperone ...
11-May-2010
Molecular Microbiology, online article
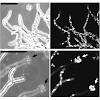
Farnesol is known for inducing apoptosis in some fungi and mammalian cells. To evaluate its potential role as an antifungal agent, we studied its impact on the human pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus. We found that growth of A. fumigatus wild type is inhib- ited, but two cell wall mutants, Dmnt1 and DglfA, are much more susceptible to farnesol. This susceptibil- ity ...
07-May-2010
International Journal of Medical Microbiology, online article
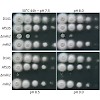
The cell wall integrity (CWI) pathway, best characterized in S. cerevisiae, is strikingly conserved in Aspergillus species. We analyzed the importance of AfMkk2, a CWI signaling kinase, for virulence and antifungal therapy in the human pathogen A. fumigatus. A mutant lacking AfMkk2 is less adherent to glass and plastic surfaces and shows increased sensitivity to ...
20-Apr-2010
The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2010, doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.103374, pp. 19029–19034, published on 20.04.2010
The Journal of Biological Chemistry, online article
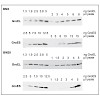
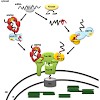
Evolution depends on the acquisition of genomic mutations that increase cellular fitness. Here, we evolved Escherichia coli MG1655 cells to grow at extreme temperatures. We obtained a maximum growth temperature of 48.5°C, which was not further increased upon continuous cultivation at this temperature for over 600 generations. Despite a permanently induced heat ...
09-Apr-2010
Molecular Cell, online article
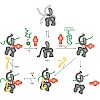
Heat shock proteins 70 (Hsp70) represent a ubiquitous and conserved family of molecular chaperones involved in a plethora of cellular processes. The dynamics of their ATP hydrolysis-driven and cochaperone-regulated conformational cycle are poorly understood. We used fluorescence spectroscopy to analyze, in real time and at single-molecule resolution, the effects ...
01-Mar-2010
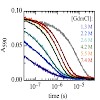
A reversible structural unlocking reaction, in which the close-packed van der Waals interactions break cooperatively, has been found for the villin headpiece subdomain (HP35) using triplet-triplet-energy transfer to monitor conformational fluctuations from equilibrium. Unlocking is associated with an unfavorable enthalpy change (ΔH0 = 35 ± 4 kJ/mol) which is ...
18-Feb-2010
Journal of Molecular Biology, online article

Small heat shock proteins (sHsps) are a ubiquitous family of molecular chaperones. They form homo-oligomers, composed of mostly 24 subunits. The immunoglobulin-like α-crystallin domain, which is flanked by N- and C-terminal extensions, is the most conserved element in sHsps. It is assumed to be the dimeric building block from which the sHsp oligomers are ...
12-Feb-2010
Molecular Cell, online article
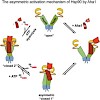
The chaperone Hsp90 is an ATP-dependent, dimeric molecular machine regulated by several cochaperones, including inhibitors and the unique ATPase activator Aha1. Here, we analyzed the mechanism of the Aha1-mediated acceleration of Hsp90 ATPase activity and identified the interaction surfaces of both proteins using multidimensional NMR techniques. For maximum ...
Redox-regulation of protein import into chloroplasts and mitochondria: Similarities and differences.
01-Feb-2010
Plant Signaling and Behavior, online article
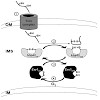
Redox signals play important roles in many developmental and metabolic processes, in particular in chloroplasts and mitochondria. Furthermore, redox reactions are crucial for protein folding via the formation of inter- or intramolecular disulfide bridges. Recently, redox signals were described to be additionally involved in regulation of protein import: in ...
28-Jan-2010
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, online article
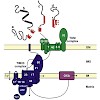
The TIM23 complex in the inner membrane of mitochondria mediates import of essentially all matrix proteins and a large number of inner membrane proteins. Here we present an overview on the latest insights into the structure and function of this remarkable molecular machine.
25-Jan-2010
Biochimica et Piophysica Acta, online article
Chloroplasts originated from an endosymbiotic event, in which an ancestral photosynthetic cyanobacterium was engulfed by a mitochondriate eukaryotic host cell. During evolution, the endosymbiont lost its autonomy by means of a massive transfer of genetic information from the prokaryotic genome to the host nucleus. Consequently, the development of protein import ...
14-Jan-2010
Nature, online article
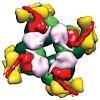
Form I Rubisco (ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase), a complex of eight large (RbcL) and eight small (RbcS) subunits, catalyses the fixation of atmospheric CO2 in photosynthesis. The limited catalytic efficiency of Rubisco has sparked extensive efforts to re-engineer the enzyme with the goal of enhancing agricultural productivity. To facilitate such ...
12-Jan-2010
J. Biol. Chem., online article
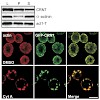
Dictyostelium discoideum Coronin7 (DdCRN7) together with human Coronin7 (CRN7) and Pod-1 of Drosophila melanogaster and Caenorhabditis elegans belong to the coronin family of WD repeat domain containing proteins. Coronin7 proteins are characterized by two WD repeat domains that presumably fold into two beta-propeller structures. DdCRN7 shares highest homology ...
01-Mar-2009
Molecular Biology of the Cell., online article
Transport of essentially all matrix and a number of inner membrane proteins is governed, entirely or in part, by N-terminal presequences and requires a coordinated action of the translocases of outer and inner mitochondrial membranes (TOM and TIM23 complexes). Here, we have analyzed Tim50, a subunit of the TIM23 complex that is implicated in transfer of ...










