Research Area B - Publications 2015
28-Dec-2015
Nucl. Acids Res., doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1517
Nucl. Acids Res., online article
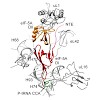
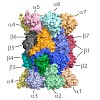
During protein synthesis, ribosomes become stalled on polyproline-containing sequences, unless they are rescued in archaea and eukaryotes by the initiation factor 5A (a/eIF-5A) and in bacteria by the homologous protein EF-P. While a structure of EF-P bound to the 70S ribosome exists, structural insight into eIF-5A on the 80S ribosome has been lacking. Here we ...
26-Nov-2015
eLife, 4:e10859. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.10859
eLife, online article
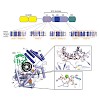
The cytosolic antiviral innate immune sensor RIG-I distinguishes 5′ tri- or diphosphate containing viral double-stranded (ds) RNA from self-RNA by an incompletely understood mechanism that involves ATP hydrolysis by RIG-I's RNA translocase domain. Recently discovered mutations in ATPase motifs can lead to the multi-system disorder Singleton-Merten Syndrome (SMS) ...
23-Nov-2015
Scientific Reports 5, Article number: 17058, doi:10.1038/srep17058
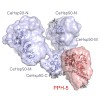
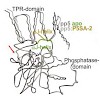
Protein phosphatase 5 is involved in the regulation of kinases and transcription factors. The dephosphorylation activity is modulated by the molecular chaperone Hsp90, which binds to the TPR-domain of protein phosphatase 5. This interaction is dependent on the C-terminal MEEVD motif of Hsp90. We show that C-terminal Hsp90 fragments differ in their regulation of ...
13-Nov-2015
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., Volume 54, Issue 52, Pages 15892–15896 , DOI: 10.1002/anie.201507266
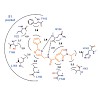
Caseinolytic protease P (ClpP) is an important regulator of Staphylococcus aureus pathogenesis. A high-throughput screening for inhibitors of ClpP peptidase activity led to the identification of the first non-covalent binder for this enzyme class. Co-crystallization of the small molecule with S. aureus ClpP revealed a novel binding mode: Because of the rotation ...
13-Nov-2015
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 54, 15888 –15891, DOI: 10.1002/anie.201506631
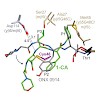
Clinically applied proteasome inhibitors induce cell death by concomitant blockage of constitutive and immunoproteasomes. In contrast, selective immunoproteasome inhibition is less cytotoxic and has the potential to modulate chronic inflammation and autoimmune diseases. In this study, we rationally designed decarboxylated peptides that covalently target a ...
10-Nov-2015
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 55, 422 –426, DOI: 10.1002/anie.201507835
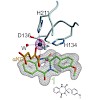
Multienzymatic cascades are responsible for the biosynthesis of natural products and represent a source of inspiration for synthetic chemists. The FeII/α-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase AsqJ from Aspergillus nidulans is outstanding because it stereoselectively catalyzes both a ferryl-induced desaturation reaction and epoxidation on a benzodiazepinedione. ...
06-Nov-2015
Journal of Molecular Biology, Volume 427, Issue 22, Pages 3572–3586, doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2015.09.012
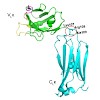
The association of light chains (LCs) and heavy chains is the basis for functional antibodies that are essential for adaptive immune responses. However, in some cases, LCs and especially fragments consisting of the LC variable (VL) domain are pathologically deposited in fatal aggregation diseases. The two domains of the LC are connected by a highly conserved ...
28-Oct-2015
THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY, VOL. 290, NO. 52, pp. 30843–30854, doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.693150

Protein kinases are the most prominent group of heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) clients and are recruited to the molecular chaperone by the kinase-specific cochaperone cell division cycle 37 (Cdc37). The interaction between Hsp90 and nematode Cdc37 is mediated by binding of the Hsp90 middle domain to an N-terminal region of Caenorhabditis elegans Cdc37 (CeCdc37). ...
16-Oct-2015
The EMBO Journal, Volume 34, Issue 22, pages 2840–2861, DOI: 10.15252/embj.201591593
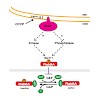
Mutations in the PTEN-induced kinase 1 (PINK1) are causative of autosomal recessive Parkinson's disease (PD). We have previously reported that PINK1 is activated by mitochondrial depolarisation and phosphorylates serine 65 (Ser65) of the ubiquitin ligase Parkin and ubiquitin to stimulate Parkin E3 ligase activity. Here, we have employed quantitative ...
16-Oct-2015
ChemMedChem, Volume 10, Issue 12, pages 1969–1973, DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.201500449
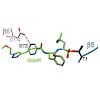
Clinical application of proteasome inhibitors (PIs) is so far limited to peripheral blood cancers due to the pronounced cytotoxicity towards all cell types. Targeted delivery of PIs could permit the treatment of other cancers along with decreasing side effects. Herein we describe the first small-molecule proteasome inhibitor conjugate for targeted delivery, ...
12-Oct-2015
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 22, 898–905, doi:10.1038/nsmb.3108
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, online article

Small heat-shock proteins, including αB-crystallin (αB), play an important part in protein homeostasis, because their ATP-independent chaperone activity inhibits uncontrolled protein aggregation. Mechanistic details of human αB, particularly in its client-bound state, have been elusive so far, owing to the high molecular weight and the heterogeneity of these ...
06-Oct-2015
BMC Plant Biology, 15:238, doi:10.1186/s12870-015-0616-0

Background: Adenine nucleotide/phosphate carriers (APCs) from mammals and yeast are commonly known to adapt the mitochondrial adenine nucleotide pool in accordance to cellular demands. They catalyze adenine nucleotide - particularly ATP-Mg - and phosphate exchange and their activity is regulated by calcium. Our current knowledge about corresponding proteins from ...
07-Sep-2015
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 22, 767–773, doi:10.1038/nsmb.3086
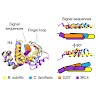
The signal recognition particle (SRP) recognizes signal sequences of nascent polypeptides and targets ribosome–nascent chain complexes to membrane translocation sites. In eukaryotes, translating ribosomes are slowed down by the Alu domain of SRP to allow efficient targeting. In prokaryotes, however, little is known about the structure and function of Alu ...
16-Jul-2015
Nature Communications, online article
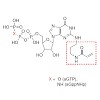
GTPases act as key regulators of many cellular processes by switching between active (GTP-bound) and inactive (GDP-bound) states. In many cases, understanding their mode of action has been aided by artificially stabilizing one of these states either by designing mutant proteins or by complexation with non-hydrolysable GTP analogues. Because of inherent ...
07-Jul-2015
Beilstein J. Org. Chem., 11, 1129–1135, doi:10.3762/bjoc.11.127
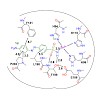
Aryl sulfonamides are a widely used drug class for the inhibition of carbonic anhydrases. In the context of our program of photochromic pharmacophores we were interested in the exploration of azobenzene-containing sulfonamides to block the catalytic activity of human carbonic anhydrase II (hCAII). Herein, we report the synthesis and in vitro evaluation of a small ...
06-Jul-2015
PLOS Genetics, DOI:10.1371/journal.pgen.1005188

The life span of non-renewing organisms is determined by the potential of their individual cells to maintain their functions while aging. Nematodes, like Caenorhabditis elegans with their 20 days of adult life, have proven to be excellent model systems to study organismal lifespan, its variability, and its regulation.
03-Jul-2015
Angewandte Chemie, online article
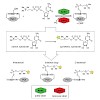
We present a new protein labeling method based on the covalent enzymatic phosphocholination of a specific octapeptide amino acid sequence in intact proteins. The bacterial enzyme AnkX from Legionella pneumophila has been established to transfer functional phosphocholine moieties from synthetically produced CDP-choline derivatives to N-termini, C-termini, and ...
24-Jun-2015
Planta, Volume 242, Issue 3, pp 733–746, DOI 10.1007/s00425-015-2352-y
Planta, online article

Main conclusion The extreme Alb3 C terminus is important for Alb3 stability in a light dependent manner, but is dispensable for LHCP insertion or D1 synthesis.
19-Jun-2015
Journal of Molecular Biology, online article

IspG is the penultimate enzyme in non-mevalonate biosynthesis of the universal terpene building blocks isopentenyl diphosphate and dimethylallyl diphosphate. Its mechanism of action has been the subject of numerous studies but remained unresolved due to difficulties in identifying distinct reaction intermediates. Using a moderate reducing agent and an epoxide ...
18-Jun-2015
Molecular Cell, online article

Small heat shock proteins (sHsps) are ubiquitous molecular chaperones that prevent the aggregation of unfolding proteins during proteotoxic stress. In Caenorhabditis elegans, Sip1 is the only sHsp exclusively expressed in oocytes and embryos. Here, we demonstrate that Sip1 is essential for heat shock survival of reproducing adults and embryos. X-ray ...
08-Jun-2015
PNAS, online article

Hsp90 is a molecular chaperone involved in the activation of numerous client proteins, including many kinases. The most stringent kinase client is the oncogenic kinase v-Src. To elucidate how Hsp90 chaperones kinases, we reconstituted v-Src kinase chaperoning in vitro and show that its activation is ATP-dependent, with the cochaperone Cdc37 increasing the ...
08-Jun-2015
JACS, online article
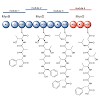
In our screening efforts to identify unique scaffolds from myxobacteria for the drug discovery process, we used LC-SPE-NMR-MS techniques to isolate six linear peptides, termed macyranone A–F, from Cystobacter fuscus MCy9118. The macyranones are characterized by a rare 2-methylmalonamide moiety and an α-amino ketone fragment including an α′,β′-epoxyketone in ...