Research Area E - Publications 2007
26-Nov-2007
After the complete sequencing of the human genome, one of the next important steps is to decipher the genetic mechanisms which allow cells to switch genes on and off. These processes are fundamental for cellular development. At the chemical level, gene silencing requires the selective methylation of of the C5-position of cytidines in DNA, and this established ...
24-Nov-2007
European Biophysics Journal, 2007, 37, 4, 435 - 45 published on 24.11.2007
European Biophysics Journal, online article

LV-peptides were designed as membrane-spanning low-complexity model structures that mimic fusion protein transmembrane domains. These peptides harbor a hydrophobic core sequence that consists of helix-promoting and helix-destabilizing residues at different ratios. Previously, the fusogenicity of these peptides has been shown to increase with the conformational ...
23-Nov-2007

CIPSM-Researcher and Speaker Thomas Carell wins the prestigious Otto-Bayer-Preis 2008 for his work of the understanding of light-triggered DNA-lesions. Thomas is a specialist for the synthesis of DNA-lesions and lesion analogues, and their incorporation into DNA-strands and the investigations of the resulting structures (x-ray, enzymatic digestion) and biological ...
22-Nov-2007
www.nature.com, free online article
12-Nov-2007
Chemical & Engineering News, online article

CISPLATIN HAS BEEN USED to treat cancer for decades. But the drug's detailed molecular interactions with the enzymes it aims to interrupts have remained obscure. In two separate papers, researchers are now reporting the first crystal structures of cisplatin complexed with two key enzymes. "For the first time, we are getting deep insight on what goes on at the ...
11-Nov-2007
www.nature.com/nsmb, online article
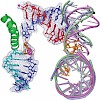
The anticancer drug cisplatin forms 1,2-d(GpG) DNA intrastrand cross-links (cisplatin lesions) that stall RNA polymerase II (Pol II) and trigger transcription-coupled DNA repair. Here we present a structure-function analysis of Pol II stalling at a cisplatin lesion in the DNA template. Pol II stalling results from a translocation barrier that prevents delivery of ...
09-Nov-2007
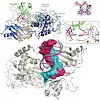
DNA polymerase eta (Pol eta) is a eukaryotic lesion bypass polymerase that helps organisms to survive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, and tumor cells to gain resistance against cisplatin-based chemotherapy. It allows cells to replicate across cross-link lesions such as 1,2-d(GpG) cisplatin adducts (Pt-GG) and UVinduced cis–syn thymine dimers. We present ...
19-Oct-2007
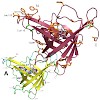
Human apolipoproteinD(ApoD) occurs in plasma associated with high density lipoprotein. Apart from the involvement in lipid metabolism, its binding activity for progesterone and arachidonic acid plays a role in cancer development and neurological diseases. The crystal structures of freeApoDand its complex with progesterone were determined at 1.8A˚ resolution and ...
05-Oct-2007
www.cell.com, online article

MicroRNAs (miRNAs) control gene expression by regulating mRNA stability and translation. Using cell-free in vitro systems, several labs have recently reported insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying miRNA-guided translational repression (Kiriakidou et al., 2007; Mathonnet et al., 2007; Thermann and Hentze, 2007; Wakiyama et al., 2007). These new ...
26-Sep-2007

Interactions of transmembrane helices play a crucial role in the folding and oligomerisation of integral membrane proteins. In order to uncover novel sequence motifs mediating these interactions, we randomised one face of a transmembrane helix with a set of non-polar or moderately polar amino acids. Those sequences capable of self-interaction upon integration ...
14-Jun-2007
www.nature.com/natureprotocols, online article
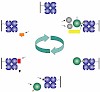
The Strep-tag II is an eight-residue minimal peptide sequence (Trp-Ser-His-Pro-Gln-Phe-Glu-Lys) that exhibits intrinsic affinity toward streptavidin and can be fused to recombinant proteins in various fashions. We describe a protocol that enables quick and mild purification of corresponding Strep-tag II fusion proteins—including their complexes with interacting ...
09-Feb-2007
Science, 2007, 315, 859-62 (pdf) published on 09.02.2007
www.sciencemag.org, online article
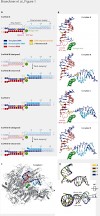
Cells use transcription-coupled repair (TCR) to efficiently eliminate DNA lesions such as UV-induced cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPDs). Here we present the structure-based mechanism for the first step in eukaryotic TCR, CPD-induced stalling of RNA polymerase (Pol) II. A CPD in the transcribed strand slowly passes a translocation barrier, and enters the ...











