Research Area E - Publications 2012
23-Dec-2012

The Tel2 (also known as Telo2) and Tti1 proteins control the cellular abundance of mammalian PIKKs and are integral components of mTORC1 and mTORC2. Here we report that Tel2 and Tti1 are targeted for degradation within mTORC1 by the SCFFbxo9 ubiquitin ligase to adjust mTOR signalling to growth factor availability. This process is primed by CK2, which translocates ...
12-Dec-2012
Mol. BioSyst., online article
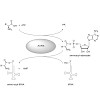
4-Hydroxyderricin is a heat labile bioactive chalcone isolated from the plant Angelica keiskei. It received attention due to its antibiotic potency against several strains of bacteria including pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus. Despite these promising pharmacological properties, the exact mode of action or the biological targets are still unknown. Here we ...
11-Dec-2012
PNAS, online article
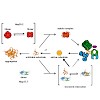
Small heat shock proteins (sHsps) are molecular chaperones that prevent the aggregation of nonnative proteins. The sHsps investigated to date mostly form large, oligomeric complexes. The typical bacterial scenario seemed to be a two-component sHsps system of two homologous sHsps, such as the Escherichia coli sHsps IbpA and IbpB. With a view to expand our ...
28-Nov-2012
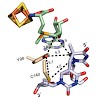
The spore photoproduct lyase is a radical SAM enzyme, which repairs 5-(α-thyminyl)-5,6-dihydrothymidine. Here we show that the enzyme establishes a complex radical transfer cascade and creates a cysteine and a tyrosyl radical dyade to establish repair. This allows the enzyme to solve topological and energetic problems associated with the radical based repair ...
21-Nov-2012
Nucleic Acids Research, online article
Recognition of the 30-splice site is a key step in premRNA splicing and accomplished by a dynamic complex comprising splicing factor 1 (SF1) and the U2 snRNP auxiliary factor 65-kDa subunit (U2AF65). Both proteins mediate protein–protein and protein–RNA interactions for cooperative RNA-binding during spliceosome assembly. Here, we report the solution structure of ...
15-Nov-2012

Recently new lysine modifications were detected in histones and other proteins. Using the pyrrolysine amber suppression system we genetically inserted three of the new amino acids ε-N-propionyl-, ε-N-butyryl-, and ε-N-crotonyl-lysine site specifically into histone H3. The lysine at position 9 (H3 K9), which is known to be highly modified in chromatin, was ...
22-Oct-2012
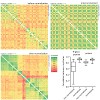
Cells secrete a large number of proteins to communicate with their surroundings. Furthermore, plasma membrane proteins and intracellular proteins can be released into the extracellular space by regulated or non-regulated processes. Here, we profiled the supernatant of 11 cell lines that are representative of different stages of breast cancer development by ...
04-Oct-2012
Angew. Chem., 2012, DOI: 10.1002/anie.201203769, Volume 51, Issue 44, pages 11162–11165, published on 04.10.2012
Transfer RNAs (tRNAs) are adapter molecules needed to translate genetic information into a peptide sequence. At the ribosome, the anticodon of each tRNA reads the corresponding codon of the messenger RNA. This anticodon– codon interaction allows the ribosome_s large subunit to catalyze amide-bond formation between the cognate amino acids present at the 3’ ...
01-Oct-2012
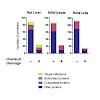
ABPP, activity-based protein profiling; ABP, activity-based probe; Cat, Cathepsin; DIC, diisopropylcarbodiimide; DIEA, N,N-diisopropyl-N-ethylamine; DMEM, dulbecco's modified eagle medium; HBTU, 2-(1H-benzotriazol-1-yl)-1,1,3,3-tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate; HOBt, hydroxybenzotriazole; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; SB, sample buffer; SPPS, solid ...
24-Sep-2012

Look, no label! Microscale thermophoresis makes use of the intrinsic fluorescence of proteins to quantify the binding affinities of ligands and discriminate between binding sites. This method is suitable for studying binding interactions of very small amounts of protein in solution. The binding of ligands to iGluR membrane receptors, small-molecule inhibitorss to ...
17-Sep-2012
Journal of Molecular Biology, online article
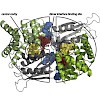
At acidic pH and in the presence of lysine, the pH sensor CadC activates transcription of the cadBA operon encoding the lysine/cadaverine antiporter CadB and the lysine decarboxylase CadA. In effect, these proteins contribute to acid stress adaptation in Escherichia coli. cadBA expression is feedback inhibited by cadaverine, and a cadaverine binding site is ...
11-Sep-2012
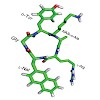
GABAA receptors are pentameric ligand-gated ion channels that are activated by the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the mammalian brain, g-aminobutyric acid (GABA).Binding of GABA results in the opening of a chloride ion selective pore, thus hyperpolarizing the postsynaptic neuron and decreasing the likelihood of action-potential firing. As such, GABAA ...
11-Sep-2012
Molecular Systems Biology, online article
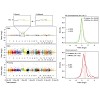
Extra chromosome copies markedly alter the physiology of eukaryotic cells, but the underlying reasons are not well understood. We created human trisomic and tetrasomic cell lines and determined the quantitative changes in their transcriptome and proteome in comparison with their diploid counterparts. We found that whereas transcription levels reflect the ...
13-Aug-2012
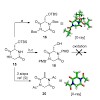
The variecolortides are a family of unusual natural products that combine motifs from a variety of biosynthetic streams. Herein, we present the gradual evolution of a convergent synthetic strategy that ultimately culminated in a reaction cascade featuring a hydrogen shift and a cycloaddition followed by a spontaneous air oxidation. Attempts to link an anthrone ...
06-Aug-2012
Angewandte Chemie, 2012, DOI: 10.1002/anie.201202090, Volume 51, Issue 32, pages 8110–8113 published on 06.08.2012
Angewandte Chemie, online article
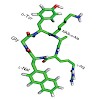
There can be only one: Using a peptoid motif obtained by shifting the arginine side chain of a pentapeptide previously developed by Fujii et al. to the neighboring nitrogen atom restricts the conformational freedom and yields a conformationally homogeneous peptide (see picture) with a 100-fold higher binding affinity to the chemokine receptor CXCR4 in the ...
26-Jul-2012

We are happy that Nature mentions CIPSMs' graduate educational program and quotes CIPSMs' CEO Oliver Baron in its highlight article about the German Excellence Initiative. pdf
13-Jul-2012
Light control of voltage-gated ion channels: We have developed red-shifted derivatives of QAQ, a powerful doubly charged photochromic blocker. These derivatives allow for remote control of Kv and Nav channel conductance with light and offer the opportunity to silence neuronal activity reversibly.
13-Jul-2012
Formation of non-covalent functional complexes of integral membrane proteins is frequently supported by sequence-specific interaction of their transmembrane helices. Here, we aligned human single-span membrane proteins with orthologs from other eukaryotes. We find that almost half of the human single-span membrane proteins contain a transmembrane helix that ...
11-Jul-2012
ChemMedChem, 2012, DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.201200229, Volume 7, Issue 8, pages 1490–1495, published on 11.07.2012
ChemMedChem, online article
Bacterial infections of skin and soft tissue represent a major health threat, especially if they are caused by multidrug-resistant strains such as MRSA. Novel treatment options for topical application are urgently needed, and even if new drug candidates are identified, their properties must match the specific physical requirements of the skin in order to ...
02-Jul-2012
Bacterial spores possess an enormous resistance to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. This is largely due to a unique DNA repair enzyme, Spore Photoproduct Lyase (SP lyase) that repairs a specific UV-induced DNA lesion, the spore photoproduct (SP), through an unprecedented radical-based mechanism. Unlike DNA photolyases, SP lyase belongs to the emerging superfamily of ...
28-Jun-2012
Angewandte Chemie, 2012, DOI: 10.1002/ange.201201193, Volume 51, Issue 29, pages 7110–7131, published on 28.06.2012
Angewandte Chemie, online article

DNA and RNA contain, next to the four canonical nucleobases, a number of modified nucleosides that extend their chemical information content. RNA is particularly rich in modifications, which is obviously an adaptation to their highly complex and variable functions. In fact, the modified nucleosides and their chemical structures establish a second layer of ...
15-Jun-2012

Thank you! CIPSM has once more been selected as a Cluster of Excellence in the German Excellence Initiative. In the next 5 years CIPSM will try to make sure, that it is here to stay. We thank all the people that helped to make that possible. More information can be found here
12-Jun-2012
New Journal of Physics, 2012, doi:10.1088/1367-2630/14/6/065006, 14 published on 12.06.2012
New Journal of Physics, online article
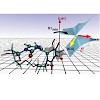
The photophysical and photochemical processes driving the formation of the ultraviolet (UV)-induced DNA Dewar lesion from the T(6-4)T dimer are investigated by time-resolved spectroscopy and quantum chemical modelling. Time-resolved absorption and emission spectroscopy in the UV revealed a biexponential decay of the electronically excited state (S1) with time ...
11-Jun-2012
The transmembrane domains of membrane fusogenic proteins are known to contribute to lipid bilayer mixing as indicated by mutational studies and functional reconstitution of peptide mimics. Here, we demonstrate that mutations of a GxxxG motif or of Ile residues, that were previously shown to compromise the fusogenicity of the Vesicular Stomatitis virus G-protein ...
01-Jun-2012

HSP90 is a central player in the folding and maturation of many proteins. More than two hundred HSP90 clients have been identified by classical biochemical techniques including important signaling proteins with high relevance to human cancer pathways. HSP90 inhibition has thus become an attractive therapeutic concept and multiple molecules are currently in ...
01-Jun-2012

Sesterterpenoids account for many bioactive natural products, often with unusual and complex structural features, which makes them attractive targets for synthetic chemists. This review surveys efforts undertaken toward the synthesis of sesterterpenoids, focusing on completed total syntheses and covering ca. 50 natural products in total.
31-May-2012
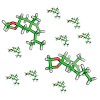
A synthetic approach to several sesterterpenoids containing an isopropyl trans-hydrindane system is presented. Its most remarkable feature is the stereochemical diversification of a common precursor through the choice of different hydrogenation conditions.
Stereoselective Total Syntheses of Herbicidin C and Aureonuclemycin through Late-Stage Glycosylation
29-May-2012
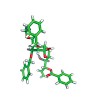
Better late than never! Two herbicidins, members of an important family of nucleoside antibiotics, have been synthesized for the first time. The route integrates a stereoselective C-glycosylation with several reagent-controlled stereoselective transformations and a surprisingly facile and highly diastereoselective late-stage N-glycosylation.
29-May-2012
5-Methylcytosine (mC) is an important, well-known nucleobase modification that is involved in many biological processes, including gene expression, genomic imprinting, Xchromosome inactivation, and suppression of transposable elements.
25-May-2012
Journal of Chemical Physics, online article
Non-adiabatic on-the-fly molecular dynamics (NA-O-MD) simulations require the electronic wavefunction, energy gradients, and derivative coupling vectors in every timestep. Thus, they are commonly restricted to the excited state dynamics of molecules with up to ≈20 atoms. We discuss an approximation that combines the ONIOM(QM:QM) method with NA-O-MD simulations to ...
18-May-2012
Mol. BioSyst., online article

Microtubules (mt) are highly dynamic polymers composed of alpha- and beta-tubulin monomers that are present in all dividing and non-dividing cells. A broad variety of natural products exists that are known to interfere with the microtubule network, by either stabilizing or de-stabilizing these rope-like polymers. Among those tubulysins represent a new and potent ...
30-Apr-2012
A concise asymmetric approach to the indeno-tetrahydropyridine core of the unusual alkaloid haouamine B allowed for an investigation of a biomimetic oxidative phenol coupling as a proposed biosynthetic step, and ultimately provided access to the published structure of the natural product. As a consequence of our synthetic studies, the structure of haouamine B has ...
27-Apr-2012
Methods for the site-specific chemical modification of proteins are currently of immense importance for the synthesis of protein–hybrid compounds for pharmaceutical and diagnostic purposes. Most of the methods rely on the reaction of free protein thiols with maleimides or the reaction of lysine side chains with activated esters. These methods provide only limited ...
19-Apr-2012
Light switch: A photochromic agonist ATA-3 (see scheme) of AMPA receptors, arguably the most important class of ionotropic glutamate receptors, is shown to be subtype selective, activates the AMPA receptor GluA2 in the dark, and is quickly turned off when irradiated with blue–green light. It can be used to effectively control neuronal activity in the mammalian brain.
16-Apr-2012
Nat. Prod. Rep., online article
The study of biologically active natural products has resulted in seminal contributions to our understanding of living systems. In the case of electrophilic natural products, the covalent nature of their interaction has largely facilitated the identification of their biological binding partners. In this review, we provide a comprehensive compilation of ...
13-Apr-2012
UV-induced cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPDs) in the template DNA strand stall transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II (Pol II). If the nucleotide excision repair machinery does not promptly remove the CPDs, stalled Pol II creates a roadblock for DNA replication and subsequent rounds of transcription. Here we present evidence that Pol II has an intrinsic ...
29-Mar-2012
Nucleic Acids Research, online article
The histone variant H2A.Z has been implicated in many biological processes, such as gene regulation and genome stability. Here, we present the identification of H2A.Z.2.2 (Z.2.2), a novel alternatively spliced variant of histone H2A.Z and provide a comprehensive characterization of its expression and chromatin incorporation properties. Z.2.2 mRNA is found in all ...
15-Mar-2012
The unusual cyclin-dependent protein kinase 5 (CDK5) was discovered based on its sequence homology to cell cycle regulating CDKs. CDK5 was found to be active in brain tissues, where it is not involved in cell cycle regulation but in the regulation of neuronal cell differentiation and neurocytoskeleton dynamics. An aberrant regulation of CDK5 leads to the ...
13-Mar-2012
The evolution of a total synthesis of the exiguamines, two structurally unusual natural products that are highly active inhibitors of indolamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), is described. The ultimately successful strategy involves advanced cross-coupling methodology and features a potentially biosynthetic tautomerization/ electrocyclization cascade reaction that forms ...
07-Mar-2012

After elucidation of the atomic details of 20S proteasomes, current research focuses on the regulatory 19S particle. In this issue of Structure, He et al. present the crystal structure of Rpn2 and use electron microscopy to examine differences between Rpn2 and Rpn1.
03-Mar-2012
Nuclear Medicine & Molecular Imaging, 2012, DOI 10.1007/s00259-011-2028-1, Volume 39, Issue 1 Supplement, pp 126-138 published on 03.03.2012
Nuclear Medicine & Molecular Imaging, online article

Imaging of angiogenesis has become increasingly important with the rising use of targeted antiangiogenic therapies like bevacizumab (Avastin). Non-invasive assessment of angiogenic activity is in this respect interesting, e.g. for response assessment of such targeted antiangiogenic therapies. One promising approach of angiogenesis imaging is imaging of specific ...
19-Feb-2012
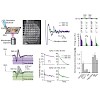
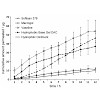
Local anesthetics effectively suppress pain sensation, but most of these compounds act nonselectively, inhibiting activity of all neurons. Moreover, their actions abate slowly, preventing precise spatial and temporal control of nociception. We developed a photoisomerizable molecule, quaternary ammonium–azobenzene–quaternary ammonium (QAQ), that enables rapid and ...
19-Feb-2012
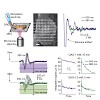
Local anesthetics effectively suppress pain sensation, but most of these compounds act nonselectively, inhibiting activity of all neurons. Moreover, their actions abate slowly, preventing precise spatial and temporal control of nociception. We developed a photoisomerizable molecule, quaternary ammonium–azobenzene–quaternary ammonium (QAQ), that enables rapid and ...
17-Feb-2012
Cell, online article

Constitutive proteasomes and immunoproteasomes shape the peptide repertoire presented by major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I) molecules by harboring different sets of catalytically active subunits. Here, we present the crystal structures of constitutive proteasomes and immunoproteasomes from mouse in the presence and absence of the epoxyketone ...
13-Feb-2012

Oxidative degradation of DNA is a major mutagenic process. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced in the course of oxidative phosphorylation or by exogenous factors are known to attack preferentially deoxyguanosine. The latter decomposes to give mutagenic lesions, which under physiological conditions are efficiently repaired by specialized maintenance systems in ...
12-Feb-2012

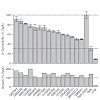
Analytical advantages of using multiple enzymes for sample digestion (MED), primarily an increase of sequence coverage, have been reported in several studies. However, this approach is only rarely used, mainly because it requires additional sample and mass spectrometric measurement time. We have previously described Filter Aided Sample Preparation (FASP), a type ...
07-Feb-2012
Angewandte Chemie, online article

Pyrrolysine is the 22nd amino acid that is encoded by the natural genetic code. In the archaebacterial family Methanosarcinaceae, its incorporation into three proteins (MtmB, MtbB, and MttB) involved in the methylamine catabolic pathway is specified by the amber stop codon UAG. The unusual amino acid was discovered in 2002 by crystallography and mass spectrometry ...
06-Feb-2012
Journal of Molecular Biology, online article
Isoprenoids derive from two universal precursors, isopentenyl diphosphate and dimethylallyl diphosphate, which in most human pathogens are synthesized in the deoxyxylulose phosphate pathway. The last step of this pathway is the conversion of (E)-1-hydroxy-methylbut-2-enyl-4-diphosphate into a mixture of isopentenyl diphosphate and dimethylallyl diphosphate ...
06-Feb-2012
Chem. Commun., online article

Cancer is the No. 2 cause of death in the Western world and one of the most expensive diseases to treat. Thus, it is not surprising, that every major pharmaceutical and biotechnology company has a blockbuster oncology product. In 2003, Millennium Pharmaceuticals entered the race with Velcades, a first-in-class proteasome inhibitor that has been approved by the ...
01-Feb-2012
A robust and scalable synthesis of a novel, cyano-substituted Danishefsky-type diene and its use in the Diels-Alder reaction with various dienophiles is reported. The diene allows for the rapid construction of highly substituted aminonaphthoquinones that occur in numerous ansamycin antibiotics.
30-Jan-2012
Journal of Biological Chemistry, online article
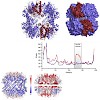
The barrel-shaped ClpP protease is a main virulence regulator in the bacterial pathogen Staphylococcus aureus. It consists of two heptameric rings forming a omo-tetradecamer with an inner chamber that houses the 14 active sites. We recently showed that SaClpP3 is able to adopt a compressed, inactive conformation. We here present the 2.3 Å resolution structure of ...
15-Jan-2012
Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, online article
Here, we report the synthesis and in depth characterization of a second generation β-lactone derived virulence inhibitors. Based on initial results that emphasized the intriguing possibility to disarm bacteria in their virulence the present study develops this concept further and analyses the potential of this strategy for drug development. We were able to expand ...
10-Jan-2012
Int. J. Cancer, 2012, DOI: 10.1002/ijc.27429, 131, 1577–1590 published on 10.01.2012
Int. J. Cancer, online article

5-Methylcytosine (5 mC) in genomic DNA has important epigenetic functions in embryonic development and tumor biology. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine (5 hmC) is generated from 5 mC by the action of the TET (Ten-Eleven-Translocation) enzymes and may be an intermediate to further oxidation and finally demethylation of 5 mC. We have used immunohistochemistry (IHC) and ...
10-Jan-2012
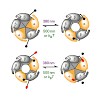
Advances in synthetic chemistry, structural biology, molecular modelling and molecular cloning have enabled the systematic functional manipulation of transmembrane proteins. By combining genetically manipulated proteins with lightsensitive ligands, innately ‘blind’ neurobiological receptors can be converted into photoreceptors, which allows them to be ...
09-Jan-2012
Angewandte Chemie, online article
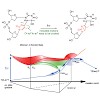
Living organisms exposed to sunlight are constantly challenged by the formation of UV-induced lesions in DNA, which induce cell death and cause mutations. UVirradiation of TpT and TpC sequences leads to the formation of two primary lesions, namely cyclobutane-pyrimidine dimers (CPD)and lesions, as depicted in Scheme 1. These lesions possess an additional ...
06-Jan-2012
The EMBO Journal, online article

Sti1/Hop is a modular protein required for the transfer of client proteins from the Hsp70 to the Hsp90 chaperone system in eukaryotes. It binds Hsp70 and Hsp90 simultaneously via TPR (tetratricopeptide repeat) domains. Sti1/Hop contains three TPR domains (TPR1, TPR2A and TPR2B) and two domains of unknown structure (DP1 and DP2). We show that TPR2A is the high ...
04-Jan-2012
Med. Chem. Commun., 2011, DOI: 10.1039/C2MD00275B, published on 04.01.2012
Med. Chem. Commun., online article
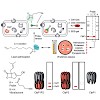
Activity-based protein profiling (ABPP) employs small molecule probes to profile their dedicated targets in complex proteomes. Unlike traditional proteomics which is limited on protein abundance, probes that selectively target the active site of certain proteins are a benign measure of protein activity and provide tools for functional analysis. ABPP probes have ...
01-Jan-2012

Tetraalkylcuprates are prototypical examples of organocopper(III) species, which remained elusive until their recent detection by NMR spectroscopy. In agreement with the NMR studies, the present electrospray ionization mass spectrometric experiments, as well as supporting electrical conductivity measurements, indicate that LiCuMe2·LiCN reacts with a series of ...










