Barrel-shaped ClpP Proteases Display Attenuated Cleavage Specificities
25-Nov-2015
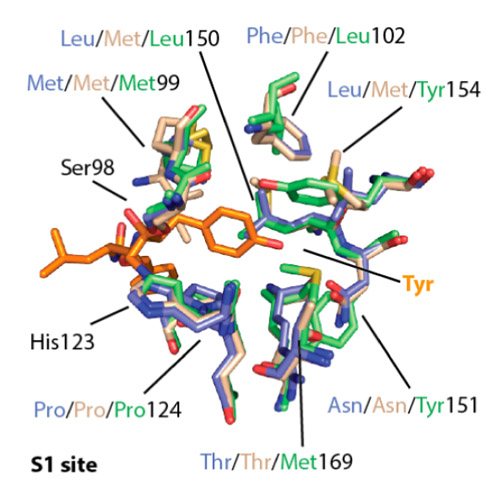
ClpP is a self-compartmentalizing protease with crucial roles in bacterial and mitochondrial protein quality control. Although the ClpP homocomplex is composed of 14 equivalent active sites, it degrades a multitude of substrates to small peptides, demonstrating its capability to carry out diverse cleavage reactions. Here, we show that ClpP proteases from E. coli, S. aureus, and human mitochondria exhibit preferences for certain amino acids in the P1, P2, and P3 positions using a tailored fluorogenic substrate library. However, this high specificity is not retained during proteolysis of endogenous substrates as shown by mass spectrometric analysis of peptides produced in ClpXP-mediated degradation reactions. Our data suggest a mechanism that implicates the barrel-shaped architecture of ClpP not only in shielding the active sites to prevent uncontrolled proteolysis but also in providing high local substrate concentrations to enable efficient proteolytic processing. Furthermore, we introduce customized fluorogenic substrates with unnatural amino acids that greatly surpass the sensitivity of previously used tools. We used these to profile the activity of cancer-patient- and Perrault-syndrome-derived ClpP mutant proteins.