Ion mobility tandem mass spectrometry enhances performance of bottom-up proteomics
08-Aug-2014
Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, 2014, doi: 10.1074/mcp.M114.041038, 13, 3709-3715, published on 08.08.2014
Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, online article
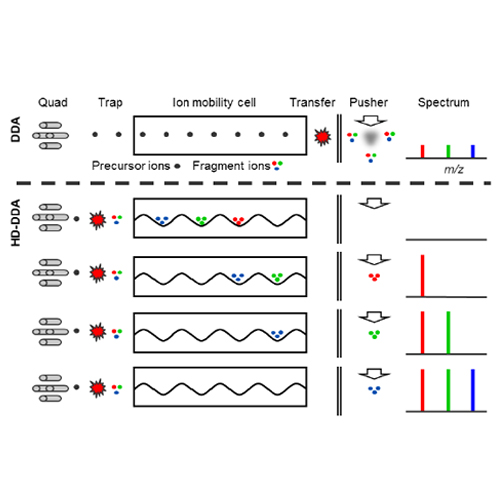
One of the limiting factors in determining the sensitivity of tandem mass spectrometry using hybrid quadrupole orthogonal acceleration time-of-flight instruments is the duty cycle of the orthogonal ion injection system. As a consequence, only a fraction of the generated fragment ion beam is collected by the time-of-flight analyzer. Here we describe a method utilizing postfragmentation ion mobility spectrometry of peptide fragment ions in conjunction with mobility time synchronized orthogonal ion injection leading to a substantially improved duty cycle and a concomitant improvement in sensitivity of up to 10-fold for bottom-up proteomic experiments. This enabled the identification of 7500 human proteins within 1 day and 8600 phosphorylation sites within 5 h of LC-MS/MS time. The method also proved powerful for multiplexed quantification experiments using tandem mass tags exemplified by the chemoproteomic interaction analysis of histone deacetylases with Trichostatin A.