Quantification of the N-glycosylated Secretome by Super-SILAC During Breast Cancer Progression and in Human Blood Samples*
22-Oct-2012
Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, 2012, doi: 10.1074/mcp.M112.023614, Proteomics, 12, 158-171, published on 22.10.2012
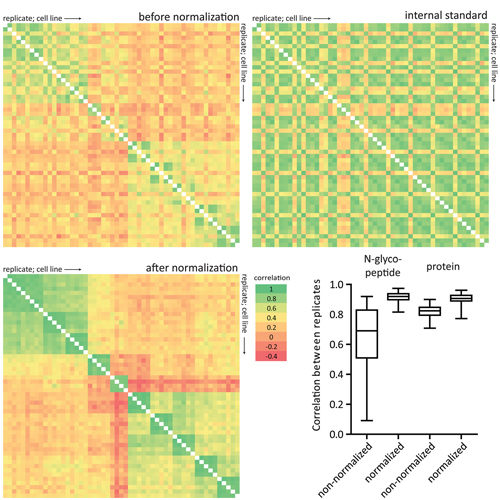
Cells secrete a large number of proteins to communicate with their surroundings. Furthermore, plasma membrane proteins and intracellular proteins can be released into the extracellular space by regulated or non-regulated processes. Here, we profiled the supernatant of 11 cell lines that are representative of different stages of breast cancer development by specifically capturing N-glycosylated peptides using the N-glyco FASP technology. For accurate quantification we developed a super-SILAC mix from several labeled breast cancer cell lines and used it as an internal standard for all samples. In total, 1398 unique N-glycosylation sites were identified and quantified. Enriching for N-glycosylated peptides focused the analysis on classically secreted and membrane proteins. N-glycosylated secretome profiles correctly clustered the different cell lines to their respective cancer stage, suggesting that biologically relevant differences were detected. Five different profiles of glycoprotein dynamics during cancer development were detected, and they contained several proteins with known roles in breast cancer. We then used the super-SILAC mix in plasma, which led to the quantification of a large number of the previously identified N-glycopeptides in this important body fluid. The combination of quantifying the secretome of cancer cell lines and of human plasma with a super-SILAC approach appears to be a promising new approach for finding markers of disease.